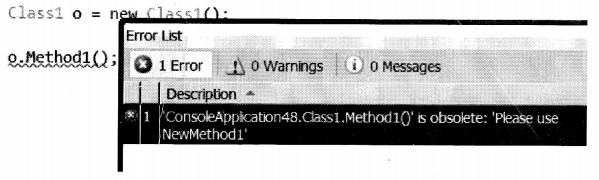
We have compiled most frequently asked Java J2EE Interview Questions which will help you with different expertise levels.
Java J2EE Interview Questions on OOPS and Core Java
Question 1.
Discuss the significance of the Java language.
Answer:
Java is the preeminent language of the Internet. Apart from this, many of its features are influencing upcoming languages such as C#. Java not only opened the door to immense possibilities on the Internet but is inherently suitable for administrative data processing (via database processing), for development using client/server architectures as well as for something it was tailor-made: industrial and loaded data processing.
Without any doubt, we can say that Java shall remain a popular programming language for many future years to come.
Question 2.
Elaborate briefly upon the evolution of Java.
Answer:
A research team at Sun Microsystems was working on the development of home automation applications that could be integrated into cellular telephones and real-time portable systems all of which were developed using C++. This type of development imposed certain restrictions due to the different hardware architectures, interconnection problems between different machines, etc. C++ was not particularly suitable for this kind of development as it is greedy on memory, lacks portability across processes, and pointer management risks the deletion of data vital to the operation of the application.
Given such problems, one of the team members, namely James Gosling endeavored to write a new programming language. Given its application domain, this language needed to be object-oriented, high performance-oriented, fast, and such to ensure portability between different types of hardware. At first, it was called C++–, then Oak, and finally Java – a slang term for “coffee” – due to the amount of coffee consumed by the developers.
Question 3.
Compare in brief C/C++, C#, and Java.
Answer:
Java derives its syntax from C. Many of the object-oriented features of Java were strongly influenced by C++. But, it would be improper to consider Java as the “Internet version of C++”. C# and Java are similar in the sense that they both share the same C++ syntax, support distributed programming, and both make use of the same object model. But, in spite of this, there are stark differences between the two.
We have already stated that Java is closely related to both C and C++, deriving its syntax from C and the object-oriented features from C++. Now, we shall see in what ways it differs from them in terms of programming.
Differences between Java & C:
- Java does not have the C keywords: size, typedef, auto, extern, register, signed, unsigned.
- Java adds new operators such as instanceof and >>> (unsigned right shift).
- Java adds labeled break and continues statements.
- Java does not support the data types struct and union.
- Java does not have an explicit pointer type.
- Java does not have a preprocessor and thus, does not support any preprocessor directive such as Refine, #include, #ifdef, etc.
Differences between Java & C++:
- Java does not support operator overloading.
- Java does not allow default arguments.
- Java does not support multiple inheritances.
- Although Java supports constructors, it does not have destructors. Instead, it has a finalize( ) function.
- Java does not allow the goto.
- Java does not have the delete operator.
- Java does not support global variables/functions as all the code in a Java program is encapsulated within one or more classes.
- The << and >> in Java are not overloaded for I/O operations.
- In Java, objects are passed by reference only. In C++, they could be passed by reference as well as by value.
- Java adds multithreading, packages, interfaces, a third comment type: the documentation comment that begins with /** and ends with */, and a built-in string type called String.
- Java does not have C++ type libraries but has its own set of API (Application Program Interface) classes.
- While both Java and C++ support a boolean data type, their implementation is different.
- In C++, a nonzero value is true while a zero value is false. But, in Java, true and false are treated as predefined literals.
- In a C++ class, the access operators apply to a group of statements while in Java, they apply only to the declarations they immediately precede.
- Both Java and C++ support exception handling. But, in C++, there is no particular requirement that a thrown exception be necessarily caught as is the case in Java.
Question 4.
Elaborate on the main features of Java.
Answer:
Some of the main features of Java include the following:-
- Simple and secure
- Portable and architecture-neutral
- Object-oriented
- Robust and multithreaded
- Interpreted and high performance
- Distributed and dynamic
Question 5.
Name and enumerate the three Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) principles.
Answer:
The three object-oriented programmings (OOP) principles are:-
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
These three principles work together in unison.
Question 6.
Distinguish between “call-by-value” and “call-by-reference”.
Answer:
There are, in general, two ways that a computer language can pass an argument to a subroutine. The first way is referred to as “call-by-value” while the second is known as “call-by-reference”. In “call-by-value”, the method copies the value of an argument into the formal parameter of the subroutine, and whence, changes made to the parameter of the subroutine have no effect on the argument. In contrast to this, a reference to an argument, and, not the value of the argument is passed to the parameter in the “call-by-reference” approach. Inside the subroutine, this reference is then used to access the actual argument specified in the call so that changes made to the parameter will affect the argument used to call the subroutine.
In Java, when a simple type is passed to a method, it is done through “call-by-value” whereas objects are passed through “call-by-reference”.
Question 7.
What is recursion? Does Java support recursion?
Answer:
Recursion is the process of defining something in terms of itself. Java does support recursion as it allows a method to call itself. Such a method is said to be recursive. A classic case of recursion is computing the factorial of a number.
Question 8.
How can you determine the size of an array?
Answer:
The size of an array, that is to say, the number of elements it can hold is found in its length instance variable.
Question 9.
How are command-line arguments passed in Java?
Answer:
In Java, all command-line arguments are passed as strings only. If you wish to pass numeric values, they must be converted to their internal forms manually.
Question 10.
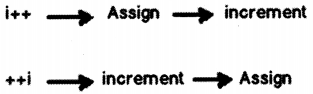
What is the difference between the prefix increment ++x and the postfix increment x++?
Answer:
The statement:-
y = y + x++;
adds the current values of x and y and assigns this result back to y. The value of x is only incremented after the value of y has been thus obtained.
On the other hand, the statement:-
y = y + ++x;
obtains the value of x, increments x, then adds that value to the current value of y, and this result is assigned to y.
You can see for yourself (by assigning some initial values to x and y) that simply changing ++x to x++ changes the results quite substantially when both of the above statements are run over a loop.
Question 11.
What is the use of short-circuit logical operators | | OR and && AND?
Answer:
Contrary to the normal counterparts | and &, the short. circuit operators | | and && evaluate the second operand only when necessary. That is to say, the result of the OR operation will always be true if the first operand is true irrespective of the second operand. Similarly, the result of the AND operation will always be false if the first operand is false irrespective of the second operand. In both these cases, | | and && do not evaluate the second operand unlike their normal counterparts I and &, which evaluate both the operands in all situations.
Question 12.
Can you name an operator in Java that takes three operands?
Answer:
The ternary operator with the most general form:-
exp1? exp2: exp3;
(if exp1 is true, exp2 becomes the value of the whole expression else exp3 becomes the value of the whole expression)
Question 13.
Can you create a ‘for’ loop without any conditional expressions? What does it amount to?
Answer:
Leaving the conditional expressions in a ‘for’ loop makes it an infinite loop that will run forever:-
for ( ; ; ) / / intentional infinite loop
{
……………….
………………
}
Question 14.
Can Objects be passed as parameters just like simple types?
Answer:
Yes! The answer to this query is in the affirmative.
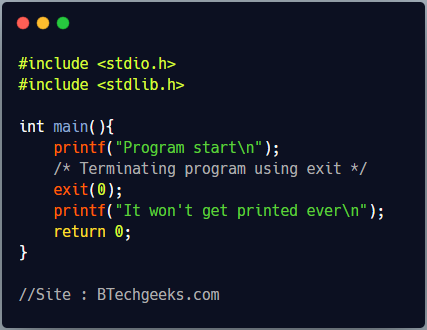
Question 15.
What do the break and continue statements do? Bring out the main point of difference between them.
Answer:
The break statement causes early termination of the loop whereas the continue statement causes an early iteration of the loop.
Question 16.
Explain the use of the keyword new.
Answer:
The keyword new is used to create objects, e.g.
House building = new House ( );
Here, building by itself does not contain the object (House). Rather, it contains a reference to it.
On the other hand, consider:
int i = 100;
Here, i contains the value 100 since i is a variable of type int, which, in turn, is a value type.
Again, consider:
douse building1 = new House ( );
House building2 = new House ( );
building2 = building1;
House building3 = new House ( );
‘building2 = building3;
After the execution of this sequence, building2 refers to the same object (House) as building3. The object (House) referred to by building1 is unchanged.
Question 17.
What are the two uses of the keyword super?
Answer:
- A subclass can call a constructor defined in its superclass by using the keyword super.
- The second use of super relates to situations in which member names of a subclass hide members by the same name in the superclass. In such a case, you can refer to the superclass member by using super. member.
Question 18.
Point out the difference between C++ and Java as regards the release of previously allocated memory.
Answer:
In C++, the delete operator is used to free memory that was previously allocated. But, Java uses a different, more trouble-free approach, viz. garbage collection.
Question 19.
What is the purpose of the finalize( ) method in Java?
Answer:
We can define a method in Java that shall be called just prior to the object’s final destruction by the garbage collector. This method is known as the finalize( ) method, which can be used in some highly specialized situations to ensure that the object is destroyed/terminated cleanly.
Question 20.
What do you understand by ‘this’?
Answer:
When a method is called, it is, by itself, passed a reference to the invoking object, i.e. the object on which the method is called. This reference is referred to as ‘this’.
Question 21.
Can you elaborate on the concept of jagged arrays?
Answer:
In general, when we create a two-dimensional array, we are creating what is a rectangular array with the length of each row being the same for the entire array, e.g. a 2 x 3 array implies an array of two rows with three elements in each row. But, Java allows you to create a special two-dimensional array called a jagged array, which is an array of arrays, where the length of each array can differ. In this way, we can have a table where the lengths of the rows differ, e.g.
int jag [ ] [ ] = new int [4] [ ];
jag [0] = new int [10]; / / length of first array is ten
jag [1] = new int [2]; / / length of second array is two
jag [2] = new int [5]; / / length of third array is five
jag [3] = new int [8]; / / length of fourth array is eight
Question 22.
Can you point out the main difference between C/C++ strings and Java strings?
Answer:
In C/C++, strings are simply arrays of characters terminated by the ‘\0’ null character whereas, in Java, the string is a built-in data type. In fact, in Java, strings are objects and thus, reference types.
Question 23.
Can the contents of strings in Java be changed?
Answer:
No, strings in Java are immutable. This might seem to be a drawback but since unused string objects are automatically garbage-collected, you can simply create a new string with the desired changes. (Refer Q. 92 also)
Question 24.
What are Java’s access modifiers?
Answer:
In Java, member access control is achieved through three access modifiers, namely, public, private, and protected. The protected modifier applies only in the case of inheritance. When a member of a class is modified by the public specifier, then that member can be accessed by any code in your program. If a member of a class is specified to be private, it can then only be accessed by other members of its class so that methods in other classes will not be able to access a private member of another class.
Question 25.
Which feature of C/C++ is similar to overridden methods in Java?
Answer:
Overridden methods in Java are similar to virtual functions in C/C++.
Question 26.
Is it possible to have a variable number of arguments in Java?
Answer:
Yes, this is a recently added new feature to Java. It was added by JDK 5. The addition of this feature has enabled formatted output in Java akin to the print( ) family of functions in C.
We might also mention here that it is possible to have a normal parameter along with the variable-length parameter but in such cases, the variable-length parameter must be the last one in the method declaration. Moreover, you cannot have a method with more than one variable-length parameter.
Question 27.
Can you declare a class as both abstract and final?
Answer:
An abstract class is incomplete by itself and relies upon its subclasses to provide a complete implementation. Whence, it is illegal to declare a class as both abstract and final.
Question 28.
When do you declare an element as protected?
Answer:
In Java, if you want to allow an element to be visible outside your current package, but only to classes that subclass your class directly, then you declare that element as protected.
Question 29.
Where does the package statement occur in a Java source file?
Answer:
The package statement must be the first statement in a Java source file.
Question 30.
Where does the import statement occur in a Java source file?
Answer:
The import statement in a Java source file must occur immediately after the package statement, if any, and before any class definitions.
Question 31.
Specify the forms of the Main ( ) method available in Java.
Answer:
The following four versions of Main ( ) are currently available in Java:-
- public static void main ( )
- public static int main ( )
- public static void main (String args[ ])
- public static int main (String args[ ])
Question 32.
Elucidate the role of the keyword static.
Answer:
In general, a class member has to be accessed through an object of its instance. But, it is possible in Java to create a member that can be used by itself, without any reference to a specific instance. To create such a member, you have to precede its declaration with the keyword static.
Question 33.
Point out any four restrictions on static methods?
Answer:
First, a static method cannot have a ‘this’ reference. Second, a static method cannot refer to super in any way. Third, a static method can directly call only other static methods. Finally, a static method can have access only to static data.
Question 34.
Which feature of Java is akin to multiple inheritances in C++?
Answer:
Interfaces in Java provide most of the functionality associated with multiple inheritances in C++.
Question 35.
Can Java interfaces be inherited?
Answer:
The answer to this query is indeed in the affirmative.
Question 36.
Give a one-line definition of an exception. What do you mean by checked and unchecked exceptions?
Answer:
An exception is a run-time error. Most of the exceptions are directly available from the JVM (such as ArithmeticException, ArraylndexOutOfBoundsException, etc.) and need not be specified in the throws list of any method. All these exceptions are known as unchecked exceptions. Then, there are other exceptions such as IllegalAccessException defined by java. lang, which must be specified in the throws statement in case a method generates them but does not handle them by itself. Such exceptions are called checked exceptions.
Question 37.
Which class is at the top of the exception hierarchy?
Answer:
Throwable.
Question 38.
Which are the two important subclasses of Throwable?
Answer:
Exception and Error.
Question 39.
Can you name the all-important subclass of Exception?
Answer:
RuntimeException.
Question 40.
What is RuntimeException?
Answer:
RuntimeException is a subclass of Exception and includes such run-time programming error conditions such as divide-by-zero and invalid array index.
Question 41.
What does the throws clause do?
Answer:
A throws clause lists all the types of exceptions that a method might throw but does not handle them by itself.
Question 42.
How is java. Is lang related to exceptions?
Answer:
Inside its standard package java.lang, Java defines several exception classes. The most general of these exceptions are subclasses of the standard type RuntimeException. Since java. lang is implicitly imported into all Java programs, most of the exceptions derived from RuntimeException are automatically available and need not be included in the throws list of any method. In terms of Java, these are known as unchecked exceptions since the Java compiler does not check to see if a method handles or throws these exceptions.
Question 43.
Can you create your own custom exceptions in Java?
Answer:
Although Java’s built-in exceptions are capable of handling the most common errors, there will still be occasions when you would like to create your own exception types specific to your applications. This is quite simply done by defining a subclass of Exception, which, in turn, is in fact a subclass of Throwable.
Question 44.
What do you understand by chained exceptions?
Answer:
Java 2, version 1.4 added the feature of chained exceptions to the exception subsystem of Java. This feature allows you to associate one exception with another where the second exception describes the cause of the first exception. For instance, take the case when an ArithmeticException occurred because of an attempt to divide by zero.
But, the actual cause of the problem was that an I/O error occurred, which caused the divisor to be set to zero. In such a scenario, the method must certainly throw an Arithmetic Exception but you also might want to let the calling code know that the underlying cause was an I/O error: chained exceptions allow you to do this and any similar situation where layers of exceptions exist, thus forming a chain.
Question 45.
Both the subclass and the superclass can have their own constructors. So, what constructor is responsible for building an object of the subclass – the one in the superclass, or the one in the subclass, or both?
Answer:
The constructor for the superclass constructs the superclass part of the object and the constructor for the subclass builds the subclass portion of the object.
Question 46.
How does a subclass call a constructor defined in its superclass?
Answer:
A subclass can call a constructor defined in its superclass by using the super keyword in the following manner-
super (Paramjit);
where Paramjit specifies any parameters required by the constructor in the superclass. Note that super must always be the first statement executed inside a subclass’ constructor.
Question 47.
In what order are constructors called in a class hierarchy?
Answer:
In a class hierarchy, constructors are called in their order of derivation, that is, from superclass to subclass.
Question 48.
What do you mean by method overriding?
Answer:
When a method in a subclass has the same name, return type, and signature as that in the superclass, it is said to override the method in the superclass and this phenomenon is referred to as method overriding in Java.
Question 49.
What do you understand by dynamic method dispatch?
Answer:
Dynamic method dispatch is the means by which a call to an overridden method is resolved at run-time rather than at compile time. It is important since Java implements run-time polymorphism this way.
Question 50.
Can you give one good reason for using overridden methods?
Answer:
Overridden methods are another way that Java implements the ‘one interface, multiple methods’ aspect of polymorphism. ’
Question 51.
Can an abstract method have a body? Can an abstract class have concrete methods (other than abstract ones)?
Answer:
While the answer to the first query is in the negative the answer to the second query is in the affirmative.
Question 52.
Can you create an object of an abstract class using new?
Answer:
An abstract class does not specify a complete implementation and whence, there can be no objects of an abstract class. Therefore, attempting to create an object of an abstract class using new will lead to a consequent compile-time error.
Question 53.
What are the three uses of the keyword final?
Answer:
- You can use final to prevent a class from being inherited by preceding the class declaration with the keyword final.
- You can use final to prevent further overriding of a method by preceding its declaration with the keyword final.
- The keyword final can be used to create what is known as final named constants.
Question 54.
What do you mean or understand by type wrappers?
Answer:
In Java, simple types such as int or char are not part of the object hierarchy. They are passed by value to methods and cannot be directly passed by reference. Moreover, there is no way for two methods to refer to the same instance of an int. There will be occasions when you need to create an object representation for one of these simple types, e.g., there are the enumeration classes,
which deal only with objects, and thus, to store a simple type in one of these classes, you must wrap the simple type in a class. To take care of this need, Java provides classes that correspond to each of these simple types. These classes essentially encapsulate or wrap the simple types within a class and whence, they are commonly referred to as type wrappers.
Question 55.
What do you mean by autoboxing and auto-unboxing?
Answer:
Beginning with JDK 5, Java added two important features, namely, autoboxing and auto-unboxing. Auto-boxing is the process by which a primitive type is automatically encapsulated (“boxed”) into its equivalent type wrapper whenever an object of that type is required. There is thus, no need to construct an object explicitly as such.
Auto-unboxing is the process by means of which the value of a “boxed” object is automatically extracted (“unboxed”) from a type wrapper when its value is required. There is thus, no need to explicitly invoke a method such as intValue( ) or doubleValue( ), etc.
Question 56.
What is the Object class in Java?
Answer:
There is one special class, Object, defined by Java, which is a superclass of all other classes. This means that a reference variable of type Object can refer to an object of any other class. Moreover, since arrays are implemented as classes in Java, a variable of type Object can also refer to an array.
Question 57.
Define an interface in Java.
Answer:
An interface defines a set of methods that will be implemented by a class. An interface, by itself, does not implement any method. In this way, we see that an interface is a purely logical construct that describes functionality without defining any implementation whatsoever.
Question 58.
What is the similarity and difference between interfaces and abstract classes?
Answer:
Interfaces are syntactically similar to abstract classes. But, in an interface, no method can have a body. Thus, an interface does not provide any implementation at all. It tells what is to be done but is completely silent about how it is to be done. Once an interface is specified, any number of classes can implement it. Moreover, one class may implement any number of interfaces.
Question 59.
How will you choose between an interface and an abstract class?
Answer:
When you can fully describe the concept in terms of ‘what it does’ without any need to specify ‘how it does it’, you should use an interface. However, if you need to include at least some implementation details, you should use an abstract class to represent your concept.
Question 60.
What is an exception handler?
Answer:
As we have already stated in the answer to Q. 36, an exception is an error which occurs at run-time. Exception handling streamlines error handling by allowing the program to specify a block of code, called an exception handler, which is executed automatically in case of an error. Exception handler eliminates the need to manually check the success / failure of each specific operation or method call. In case an error occurs, it is processed / handled by the exception handler gracefully.
Question 61.
Can you elaborate on the consequences of an uncaught exception?
Answer:
In general, if your program does not catch an exception, it will be caught by the run-time system, which, in turn, will report an error and terminate the program abnormally / ungracefully.
Question 62.
What is the major benefit of exception handling?
Answer:
One of the major benefits of exception handling is that it enables your program to respond to an error and then continue running, that is, handle the error gracefully, and then continue further.
Question 63.
Can you have a try block followed by a finally block with no catch clauses?
Answer:
Syntactically, when a finally block follows a try block, no catch clauses are technically required. In such a case, the finally block gets executed after exit from the try block, but no exceptions are handled in such a case / event.
Question 64.
Explain the concept of an inner class.
Answer:
Classes present inside another class are termed inner classes. A point to note is that inner classes increase the complexity of code and must be used only if absolutely necessary. In this context, it would be worthwhile to mention that inner classes are used to implement adapters in an AWT program.
class X
{
int x;
public void do( )
{ }
// Inner class
Class Y
{
public void done( )
{
/* can access the instance variables of the outer class */
x = 100;
}
}
}
Question 65.
Explain the concept of anonymous classes.
Answer:
An anonymous class is an inner class without a name. An anonymous class, in general, makes the code difficult to read and understand. Its use must be limited to very small classes (with a method or two) and whose use is well understood such as in the case of the AWT event¬handling adapter classes.
Question 66.
What types of variables are allowed in an interface?
Answer:
All the variables in an interface must be public, static, and final, that is to say, constants.
Question 67.
Are there any restrictions imposed on interfaces vis-a-vis classes?
Answer:
An interface is akin to a class with a few restrictions including the following:-
- As mentioned in the previous problem, all variables in an interface must be public, static, and final, i.e. constants.
- All methods in an interface are implicitly declared public and abstract.
Another point to note is that a class can inherit multiple interfaces.
Question 68.
What is a stream in Java?
Answer:
Java programs perform Input / Output through streams. A stream is an abstraction that produces/consumes information. A stream is liked a physical device by the I/O system. It is useful to note that all streams behave in the same manner irrespective of the physical device they might be linked to.
Question 69.
Compare and contrast byte streams with character streams.
Answer:
The following four are the major points of difference between Byte Streams and Character Streams:-
- java.io.InputStream and java.io.OutputStream are the base byte streams while java.io.Reader and java.io. Writer are the base character streams.
- Byte streams are 8 bit streams while character streams are 16 bit Unicode streams.
- In byte streams, method names end with the suffix InputStream or OutputStream while in case of character streams, method names end with the suffix Reader or Writer.
- Since character streams are Unicode, they are internationalized and more efficient than byte streams.
Question 70.
Elucidate the benefits of the streams.
Answer:
The streaming interface to I/O in Java provides a clean abstraction for a complex and often cumbersome task. The composition of the filtered stream classes allows you to dynamically build the custom streaming interface to suit your data transfer requirements. Java programs written to adhere to the abstract, high-level InputStream, OutputStream, Reader, and Writer classes will function properly even in the future when new and improved concrete stream classes are invented.
This model works very well even when we switch from a file system-based set of streams to the network and socket streams. Moreover, serialization of objects is expected to play an increasingly important role in the future Java programming. In fact, Java’s serialization I/O classes provide a portable solution to this sometimes tricky task/proposition.
Question 71.
Name the predefined I/O streams in Java.
Answer:
System.in, System.out, and System.err are the three predefined I/O streams in Java. By default, System.in refers to the keyboard while System.out and System.err refer to the console.
Question 72.
Name the two byte streams and the two character streams related to File I/O in Java, respectively.
Answer:
File Input St ream & FileOutputStream are the two byte streams and FIleReader & FileWriter are the two character streams, respectively, related to File I/O in Java.
Question 73.
How is binary data read and written?
Answer:
Binary data is read and written using the DatalnputStream and DataOutputStream streams, respectively.
Question 74.
Name the two classes at the top of the byte stream classes.
Answer:
InputStream and OutputStream.
Question 75.
Name the two classes at the top of the character stream classes.
Answer:
Reader and Writer.
Question 76.
Does Java have a generalized console input formatter akin to the standard C function scanf() or the C++ input operators?
Answer:
Yes, added by JDK 5 recently Java has the Scanner class which reads formatted input and converts it into its binary form. The Scanner class is the complement of the Formatter class of Java which has made formatted output in Java very easy akin to the printfO style of functions in C/C++.
Question 77.
Elucidate the New I/O system.
Answer:
Java 2, version 1.4 added a new way to handle I/O operations. Called the new I/O APIs, it supports a channel-based approach to I/O operations. The new I/O (NIO) system is built on two foundational items, viz. buffers and channels. A buffer holds data. A channel represents an open connection to an 1/O device, such as a file or a socket. In general, to use the NIO system, you obtain a channel to an I/O device and a buffer to hold data. You then operate on the buffer, inputting / outputting data as needed. We must, at this stage, sound a caveat as to whether NIO is the future of 1/O handling? The channel/buffer based NIO approach is currently designed to supplement, and not supplant the traditional and standard stream-based I/O mechanisms.
Question 78.
What types of comments are supported by Java? Does it support documentation comments?
Answer:
Java supports three types of comments – the first two are // and /* */• The third type is called a documentation comment. A documentation comment begins with /** and ends with */. Using such documentation comments, you can embed information about your program into the program itself; and, later on, you can use the javadoc utility program to extract this information and put it into an HTML file.
Question 79.
Define a package.
Answer:
A package is a container for classes that is used to keep the class name space compartmentalized.
Question 80.
Can you create a hierarchy of packages?
Answer:
You can indeed create a hierarchy of packages. To do so, simply separate each package name from the one above it by using a period. The most general form of a multileveled package statement is as follows:-
package pkg1[.pkg2[.pkg3.[pkg4]]];
Note that a package hierarchy must be reflected in the file system of your Java development system.
Question 81.
What does the Math class contain?
Answer:
The Math class contains all the floating-point functions that are used for geometry and trigonometry such as sin( ), as well as several general-purpose methods such as sqrt( ).
Question 82.
What do you mean by generics?
Answer:
Generics imply parameterized types. They provide a streamlined and type-safe approach to deal with different data types as also promote reusability of code. Generics were introduced by JDK 5 and are somewhat similar to templates in C++.
Question 83.
How is java.util useful?
Answer:
The java.util package contains one of Java’s most powerful subsystems, viz. collections. In addition to collections, java.util contains a wide assortment of classes and interfaces, which support a broad range of functionality such as generating pseudorandom numbers, manipulating date and time, observing events, manipulating sets of bits, and tokenizing strings. These classes and interfaces are used throughout the core Java packages and are, of course, available for use in the programs you write.
Question 84.
Elucidate the utility of collections.
Answer:
Collections simplify many programs by providing off-the-shelf solutions to several common but at times difficult to develop data structures. For instance, there are built-in collections that support dynamic arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, and hash tables.
Question 85.
On what principle does a Stack operate?
Answer:
Stack is a First-in, Last-out list. To visualize a stack, imagine a stack of plates on a table. The first plate put down is the last one to be retrieved.
Question 86.
What is the principle behind the Queue?
Answer:
Queue is a First-in, First-out list, i.e. the first item put in a queue is the first item retrieved from it. Queues are common in real life, e.g. lines at a bank or railway reservation center are queues.
Question 87.
What is a Hashtable?
Answer:
Hashtable creates a collection which uses a hash table for ‘storage (the hash table, in turn, stores information using a mechanism known as hashing).
Question 88.
What is the ArrayList class?
Answer:
The ArrayList class supports dynamic arrays, which can grow or shrink as per the user requirements.
Question 89.
Should collections be limited to “large jobs” such as corporate databases, inventory systems, or mailing lists?
Answer:
Collections need not be reserved for only the “large jobs” such as corporate databases, inventory systems, or mailing lists. They are equally effective when applied to smaller jobs, e.g., a TreeMap would be ideal to hold the directory structure of a set of files and a TreeSet would be an excellent choice for storing project-management information.
Question 90.
How can you obtain an Array from an ArrayList?
Answer:
When working with ArrayList, you might want to obtain an actual array, which contains the contents of the list. You can easily accomplish this by calling the toArrayi) method.
Question 91.
Are the == and the equals( ) method the same? If not, point out the difference between the two.
Answer:
It is important to understand that the equals( ) method and the = = operator perform two different operations. While the equals( ) method compares the characters inside a String object, the = = operator compares two object references to see whether they refer to the same instance.
Question 92.
How can you create a string in Java that is mutable?
Answer:
A mutable string in Java can be created by means of the StringBuffer class. In the StringBuffer class, characters can be inserted in the middle or appended to the end of a string.
Question 93.
Can an enumeration be used to control a switch statement?
Answer:
Yes, enumerations can easily be used to control a switch statement. Of course, all of the case statements must use constants from the same enum as that used by the switch expression.
Question 94.
Can you assign floating point values to integers in Java as in C/C++?
ANS.
No! Not at all!! This is due to the fact that Java is a very strongly typed language unlike C/C++.
Question 95.
How will you declare a three-dimensional array of shorts and a string variable called surname in Java? How will you determine the size of an array?
Answer:
A three-dimensional array of shorts can be declared in Java in the following manner:-
short s_arr[ ][ ][ ];
A string variable called surname can be declared as:-
String surname[ ];
In Java, the size of an array can be determined by means of the property called length.
Question 96.
Can variables in the inner scope have the same name as the ones in the outer scope in Java as in C/C++?
Answer:
No! Not at all!! In C/C++, there is no such restriction. However, the designers of Java opined that such “name hiding” could very well lead to programming errors and whence, disallowed it.
Question 97.
Does Java have a foreach loop like C#?
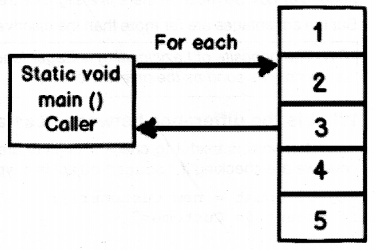
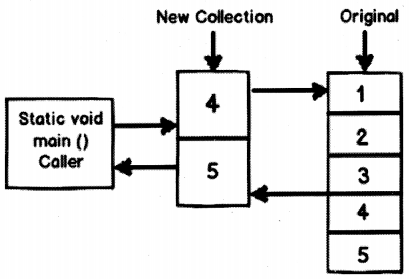
Answer:
JDK5 introduced thefor-each style loop as a simple enhanced version of the ‘for’ loop unlike C# which uses the foreach keyword. The major advantage of this is that no keyword is required and no pre-existing legacy code is broken.
The most general form of for-each style loop is:
for (var_type var_name : coll)
{
statement(s);
}
where, var_type and varjname specify the type and name of the iteration variable and the collection being cycled through is referred to by coll.
Question 98.
What are the two uses of the keyword ‘super’?
Answer:
The Java keyword, super, can be used in two distinct ways. Its first use is to call/ invoke a super class constructor. Its second use lies in accessing a member of the superclass that has been hidden by a member of the subclass having the same name.
A subclass can call a constructor defined in its immediate superclass by using super as given below:
super(argumentjist);
where, argumentJist specifies any arguments needed by the constructor in the superclass. Note that super() must be the first statement executed in the constructor of the subclass always. Also, note that since constructors can be overloaded, super() can be invoked using any form defined by the superclass. The constructor that matches the parameters/arguments shall be the one to get executed.
Now, we introduce you to the second use of super that acts in a manner similar to this except for the fact that it always refers to the superclass of the subclass in which it is used. The most general form of this usage is:
super.member
where, member can either be an instance variable or a method. This form of super applies mostly to cases in which member names of a subclass hide members by the same name in the superclass.
Question 99.
Does Java support formatted output akin to the printfO style function in C/C++? If yes, when did Java begin to have this facility and why it could not provide it earlier?
Answer:
With the release of JDK 5 (Java Development Kit 5), Java added a new capability, viz. the ability to easily create formatted output akin to the printfO style of functions in C/C++. This feature was implemented using the Formatter class of Java.
You might wonder why Java was not able to earlier provide such a facility. The simple reason was that the printfO style formatting requires the use of variable-length arguments (varargs), which Java did not support before JDK 5.
Once varargs became available with the release of JDK 5, it was easy pickings to add a general- purpose formatter. At the roots of Java’s formatted output is the Formatter class, which provides format conversions that let you display numbers, strings, date and time in almost every format as per your requirements very much similar in fashion to the printfO function of C/C++.
The Formatter class works by converting the binary form of data used by a program into formatted text. It stores this text in a buffer from where it can be obtained any time you need. The buffer may be supplied explicitly or you can let the Formatter supply it on its own. Formatter may be constructed in a variety of ways including the following:-
Formatter( )
Formatter(Appendable buf)
Formatter(String file) throws FileNotFoundException
Formatter(File outF) throws FileNotFoundException
Formatter(OutputStream outStrm)
where, buf specifies a buffer for the formatted output, file specifies the name of the file which shall receive the formatted output, outF specifies a reference to an output file that shall receive the output, and outStrm specifies a reference to an output stream which shall receive the output.
After creating the Formatter, you can use the following forma t( ) method to create a formatted string:-
Formatter format( String fmtString, Object… args)
where, fmtString contains either character which is copied as such to the output buffer or format specifiers such as %d for integers, %/for floating-point data and %s for strings.
An integer placed between the % sign and format conversion code acts as the minimum field-width specifier. The default padding is done with spaces. If you want to pad with 0’s, place a 0 before the field-width specifier, e.g., %05d will pad a number of less than five digits with 0’s so that its length is five.
By default, all output is right-justified. You can force output to be left-justified by placing a minus sign directly after the % sign, e.g., %-10.2f left-justifies a floating point number with two decimal places in a 10-character field.
When displaying large numbers, it is often useful to add a comma separator/flag, e.g., ‘ 4337788990.23 is more easily read as 4,337, 788,990.23. Formatter lets you achieve this very easily. Formatter also includes a very useful feature that lets you specify the argument to which a format % specifier applies. In other words, it allows you to use an argument index.
Question 100.
Can you elaborate on the ‘why’ of Java?
Answer:
Java serves both as a programming language as well as a platform. As a programming language, Java is simple, object-oriented, distributed, interpreted, robust, secure, architectnre- neutral, portable, high performance based, multithreaded and dynamic. By definition, a platform is a hardware/software environment in which a program can be run. The majority of present day
platforms are a combination of hardware (the machine) and software (the operating system).
The Java platform is quite different in the sense that it consists only of a software component that can be run on varying hardware. It consists of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and the Java Application Programming Interface (JAVAAPI).
Java is simple with syntax similar to that of C and C++ but without their semantic complexity that make them confusing and insecure. Thus, there is no need for pointer management etc. Java is object-oriented unlike C but-likewise C++.
Java is distributed in the sense that network access protocols like TCP/IP, UDP, HTTP, and — FTP are supplied with it that allows for the development of client/server model in order to access
data on a distant/remote machine. Once again, a Java program does not operate in the normal way.
Rather, it is interpreted by the JVM. Java achieves robustness by strict program checking during compilation as well as execution. The Java code is verified both during compilation and run-time by the interpreter making it free from errors and ensuring security.
Java is inherently architecture-neutral as the Java compiler produces Java bytecodes independent of any specific environment. The primary data in Java is primarily of the same size (generally IEEE754) ensuring portability across varying platforms. Although the Java program is interpreted resulting in it being slow to a degree but, still, Java uses JIT (Just In Time), a code interpretation optimizing technique resulting in almost the same performance as C++.
Java introduces multithreading, a concept that allows for many things/applications being run simultaneously and increases response time. Finally, in Java, one doesn’t have to edit links (mandatory in C++) resulting in executables having a lower memory size. Thus, Java is dynamic as well!
The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is the base of the Java platform and is essential for running the Java programs. It is compatible with any type of computer machine. The JVM undertakes the loading of Java bytecodes, classes, memory management, security management and, if necessary, interfacing with native code such as C. The JAVAAPI package contains a collection of prefabricated software components that supply a number of functions like the management of graphical interface etc.
The Java Application Interface is organized as a collection of packages just as libraries in C/ C++. Each package has Java classes that are predefined language objects directly reusable. The Java platform consisting of the JVM and the JAVAAPI is the link between the hardware and the Java program.
To compile Java source code, we need to use the compiler dedicated to our machine. After compilation, the file remains independent of the hardware platform and the operating system. The interpreter rims Java programs.
To run Java applets, the interpreter is incorporated into Java compatible Web browsers such as Hotjava (refer Chapter 2), Netscape Navigator etc. To run independent stand alone Java applications, we need to run the virtual machine (JVM) supplied with the Java development Kit (JDK) or the Java runtime Environment (JRE).
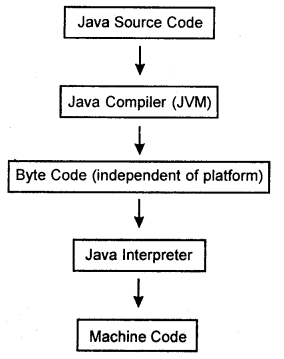
As discussed above, a Java program is independent of the operating system/platform on which it is run. This is achieved by means of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) that converts the original source code into bytecodes (which is platform independent). Finally, the Java interpreter on the concerned operating system converts these bytecodes into machine code which can be run on that particular machine. Figure 1 illustrates all this.
Question 101.
Can you explain the difference between a .class file and an .exe file?
Answer:
There is basically one main point of difference between the two. While a .class file contains bytecodes for the JVM and is thus system independent, an .exe file contains machine language for the microprocessor and is thus system dependent.
Question 102.
What do you understand by an API document? Elucidate.
Answer:
An API document is essentially an .html file having complete details of all the features of a software/product/technology. It is very much handy for the users in using the relevant software/product/technology.
Question 103.
Can you explain the difference between the #include statement of C/C++ and the import statement of Java?
Answer:
The import statement of Java is a much better option than the #include statement of C/C++ since the import statement makes the JVM go to the standard Java library, run the code over there, and finally, substitute the result into the Java program thus avoiding any wastage of memory/processor’s time while the #include directive of C/C++ makes the compiler go to the standard C/C++ library and copy the code from the header files into the C/C++ program leading to a considerable increase in the program size, which, in turn, results in wastage of memory and the processor time.
Question 104.
Suppose, String args [ ] is not written in the main( ) method; will the program still run? Elucidate.
Answer:
Suppose, we write the main( ) method without String args [] as follows:-
public static void main( )
The compiler will not report any error in such a case but the Java Virtual Machine environment, which always looks for the main( ) method with String args [ ] as parameter, will not be able to recognize the main( ) method in such a case and, whence, the program shall not run/ execute.
Question 105.
Is it possible in Java to call the main( ) method of a class from another class? Elucidate.
Answer:
Yes! It is very much possible!! This is achieved by the use of the relevant clas$mme.main( ). Note that at the time of calling main( ), you will have to pass a string type array to it.
Question 106.
Is it possible in Java to compile and run a program without the main( ) method? Elucidate.
Answer:
Yes! It is very much possible!! This is achieved by the use of a static block in the relevant Java program.
Question 107.
Can you explain the difference between the float and double data types of Java?
Answer:
The float data type can store up to seven digits after the decimal point accurately; on the other hand, the double data type can store up to fifteen digits after the decimal point accurately.
Question 108.
Can you explain the difference between the return statement and the System. exit(0) statement of Java?
Answer:
The return statement can be used anywhere in a method to come out of it while System.exit(0) can be used anywhere in a method to come out of the Java program itself.
Question 109.
Can you explain the difference between the System. exit(1) statement and the System.exit(0) statement of Java?
Answer:
The System.exit(1) statement is used to exit the Java program abnormally because of some error encountered during its execution while System.exit(0) is used to exit the Java program normally without any error.
Question 110.
Can you explain the difference between the System.err and System.out?
Answer:
Although both System.out and System.err send messages to the monitor, by default, the difference lies in the fact that System.out displays normal output while System.err displays error messages.
Question 111.
What are the types of memory available in Java; incidentally, on which memory are arrays created in Java?
Answer:
There is no static memory in Java; there is only dynamic memory. As such, everything (objects, variables) as well as arrays are created on dynamic memory only.
Question 112.
Can you consider class as a data type?
Answer:
Yes! Indeed, a class is a user-defined data type.
Question 113.
What, according to you, is String – a class or a data type?
Answer:
String is a class in java.lang package. But as mentioned in the previous question, a class can be taken to be a data type as well. Whence, String can be considered as a data type too.
Question 114.
Can you explain the difference between the String class and the StringBuffer class of Java?
Answer:
There are two points of difference between String and StringBuffer classes of Java:-
- String class objects are immutable so that their contents are not modifiable; StringBuffer class objects are mutable so that their contents are modifiable.
- The methods that directly manipulate the contents of objects are available only in the StringBuffer class.
Question 115.
Can you explain the difference between the StringBuffer and StringBuilder classes of Java?
Answer:
StringBuilder is identical to StringBuffer with one important exception, viz. it’s not synchronized, which, in turn, implies that it’s not thread-safe. The main advantage and benefit of StringBuilder is faster performance. But, there is a caveat. In cases where you are using multithreading, you must make use of StringBuffer instead of StringBuilder since only StringBuffer is synchronized.
Question 116.
What do you understand by hash code? How can you determine the hash code of an object?
Answer:
Hash code is a unique identification number assigned to objects by the JVM. It is created based on the basis of the location of the object in memory and is unique for all objects with the sole exception of String objects. The hash code of an object can be determined using the hashCode( ) method of the Object class in java.lang package.
Question 117.
Can a class in Java be declared private?
Answer:
By declaring a class as private, it becomes unavailable to the Java compiler resulting in a compile-time error. However, inner classes can be declared to be private.
Question 118.
What do you understand by factory methods? Elucidate.
Answer:
A method that creates and returns an object to the class to which it belongs is known as a factory method. A single factory method can replace several different constructors in the class by accepting different options from the user while in the process of creating the object.
Question 119.
In what different ways can you create an object in Java?
Answer:
You can create an object in Java in any of the following ways:-
- By the use of the new operator;
- By cloning an already available object;
- By the use of the newInstance( ) method; and,
- By the use of factory methods.
Question 120.
What is the main point of difference between method overloading and method overriding?
Answer:
Writing two or more methods with the same name but different signatures is referred to as method overloading while writing two or more methods with the same name and the same signatures is referred to as method overriding.
Question 121.
Can you name the super class for all classes inclusive of your classes as well?
Answer:
The Object class.
Question 122.
Can you write an interface without any methods?
Answer:
YES!
Question 123.
Can you name the method used in cloning?
Answer:
The clone( ) method of the Object class.
Question 124.
What is an abstract method/class?
Answer:
An abstract method is simply a method without any body. It is generally used when the same method has to carry out different tasks based upon the object calling it. An abstract class is simply a class with one or more abstract methods.
Question 125.
Can you forcibly implement only the features of your class; if yes, how?
Answer:
This can be easily achieved by using an abstract class or by the use of an interface.
Question 126.
Can one interface be implemented from another?
Answer:
NO! Not at all!!
Question 127.
Do you think you need to write both the following statements:
- import java.awt.event.*;
- import java. awt. *;
Or, the second one alone is sufficient? Give appropriate reason(s) for your answer.
Answer:
event is a sub-package of java.awt package. However, when a package is imported, its sub-packages are not imported into the program by themselves. Whence, for every package or sub-package, you need to write a separate import statement. Therefore, if you want to import the classes and interfaces of both the java.awt.event and java.awt packages, you should include both the import statements in your program.
Question 128.
What do you understand by CLASSPATH? Elucidate.
Answer:
CLASSPATH is an environment variable which tells the Java compiler as to where to look for the class files to import.
Question 129.
What do you understand by a JAR file?
Answer:
A JAR or Java Archive file, as it is called, is a file containing compressed versions of different .class files, audio files, image files, and directories.
Question 130.
What is the scope of the default access specifier?
Answer:
Default members are available within the same package but not outside it.
Question 131.
Bring out the difference between an exception and an error.
Answer:
An exception is an error that can be handled gracefully but an error means a condition that cannot be handled and the program can do nothing to handle the situation.
Question 132.
Bring out the difference between throw and throws.
Answer:
throw is used to throw an exception explicitly and handle it using a try-catch block while throws is used to throw the exception out of a method without handling it there and then.
Question 133.
Can you name the Wrapper class with only one constructor?
Answer:
Character wrapper class.
Question 134.
Can a primitive data type be stored into a collection?
Answer:
NO! Not at all!! Collections can store only objects.
Question 135.
Bring out the major difference between ArrayList and Vector.
Answer:
ArrayList object is hot synchronized by default while Vector object is synchronized by default.
Question 136.
What do you understand by serialization? Are there any variables which cannot be serialized?
Answer:
Serialization is essentially the process of storing object contents into a file; static and transient variables cannot be serialized.
Question 137.
What do you understand by jenumerations?
Answer:
Enumerations were added to Java with the release of JDK 5. An enumeration is a way of assigning names to integer constants..
To give you a practical example of the need for enumerations, imagine a scenario where you wanted to represent the seasons of the year in a program. You could very well use the integers 0, 1,2, and 3 to represent spring, summer, autumn, and winter respectively. This solution would work but it is not very innovative, e.g., if you used the integer value 0 in the program code, it would not be very obvious that a particular 0 represented spring.
Furthermore, it would also not be a very robust solution to the problem, e.g., if you declare an integer variable called season, there is nothing to prevent you from assigning the variable season any legal integer value other than 0,1, 2, or 3. Enumerations offer a much better solution. You can create an enumeration (sometimes called an enum type), whose values would be limited to a set of symbolic names, e.g. in this particular case, it could be:
enum season!spring, summer, autumn, winter}
The most general form of an enumeration is:
enum enum_name {enumjist} // notice the keyword ‘enum’!
where enum_name is the name of the said enumeration and enumjist is a comma-separated list of identifiers.
Java enumerations are class types. Although an enum is not instantiated using new, it has more or less the same capabilities as other classes. This feature adds to the power of Java enumerations in a big way, e.g., you can give them constructors, add instance variables/methods, and even implement interfaces.
It is important to realize that each enum constant is an object of its enumeration type so that when you define a constructor for an enum, the constructor is invoked when each enum constant is created.
Question 138.
What do you understand by annotations?
Answer:
JDK 5 introduced a new feature into the Java language, viz. annotations (metadata) by means of which you could embed supplemental information into a source file.
In fact, this information is itself called an annotation, which leaves the semantics/actions of a program unchanged but can be used by various tools both during deployment and development, e.g., an annotation can be processed by a source-code generator.
An annotation is created by means of a mechanism based on the interface. To declare an annotation, say, MyAnnotation, we proceed as follows:
// A simple annotation type'
@interface MyAnnotation
{
String s( );
int value( );
}
Take note of the @ preceding the keyword interface. This indicates to the compiler that an annotation is being created. Now, take note of the two members, s( ) and value( ). All annotations
solely consist of method declarations. But, you don’t provide bodies for these methods; Java implements these methods instead. Also, the methods act much like fields as we shall see shortly.
Once an annotation is declared, it can be used to annotate any declaration, which means that any type of declaration can have an annotation associated with it, e.g., classes, methods, fields, parameters, and enum constants may be annotated. In fact, even an annotation may be annotated. In all cases, the annotation comes before the rest of the declaration. When applying an annotation, its members are given values, e.g., here is an example of MyAnnotation being applied to a method:
// Annotate a method
@MyAnnotation(s = "string”, value - 999)
public static void my Method( )
{
// ...............
}
Thus, MyAnnotation has linked with the method my Method( ). Take note of the annotation syntax. The name of the annotation, preceded by a @1, is followed by a parenthesized list of member initializations. Also, take note of the fact that no parentheses follow s or value in this assignment of initial values so that annotation members act like fields in this regard.
Question 139.
What do you understand by a generic type?
Answer:
A generic type is a class/interface which can act on any data type. In other words, it is type-safe.
Question 140.
Bring out the major difference between window and frame.
Answer:
A window is a frame without any borders/title while a frame does have borders/title.
Question 141.
Elucidate the MVC architecture in JFC/swing.
Answer:
MVC or Model-View-Controller, as it is called, is essentially a model used in swing components, wherein, Model is the data of the component, Vieiv is its appearance while Controller is a mediator between the. model and the view.
In other words, MVC is the separation of the model of an object from its view as well as how it is controlled.
Question 142.
Enumerate the various window panes available in the swing.
Answer:
The various window panes available in the swing are enumerated below:-
- Content pane;
- Glass pane;
- Layered pane; and,
- Root pane.
Question 143.
What do you understand by a layout manager?
Answer:
A layout manager essentially is a class helpful in arranging components (in a specific/ particular way) in a frame/container.
Question 144.
Consider the following Method whose sole purpose is to find out if the argument passed to it is odd:
public static boolean odd(int k)
{
return k % 2 ==1;
}
Does the Method work?
Does the Method work?
Answer:
An odd number is an integer that leaves 1 as the remainder when divided by 2. The expression k % 2 computes this remainder; so, it looks like that this Method ought to work. But, it returns the wrong answer one-quarter of the time. This is so since half of the integer values are negative and when half of these negative integer values are divided by 2, the remainder is -1, not 1.
Question 145.
Can you provide declarations for two variables z and k such that:
z+- k;
is legal while
z = z + k;
is illegal?
Answer:
Consider:
short z = 0;
int k – 1234;
The compound assignment:
z +- k; // contains a hidden cast
// but compiles without error
ivhile the corresponding simple assignment:
z = z + k; // requires explicit cast
// and won’t compile
// due to possible loss of precision
Question 146.
Can you provide declarations for two variables z and k such that:
z+= k; is illegal
while
z = z + k; is legal?
Answer:
Consider:
Object z = “BE”;
String k = “YOURSELF ALWAYS!”;
The compound assignment:
z += k; // is illegal
// since LHS has an object reference type
// other than String
while the corresponding simple assignment:
z – z + k; I //is legal since RHS is of type String
// and String is an assignment
// compatible with-Ohject
Question 147.
Consider the following Program:
public class Hurrah
{
public static void main(String args [ ])
{
System.out.printlnC'H" + "A");
System.out.printlnCH' + 'A');
}
}
What does the Program print?
Answer:
HA
137
Question 148.
Consider the following Program:
public class Browser
{
public static void main(String args [ ])
}
System.out.printC explore":);
http://www.yahoo.mail;
System.out.printlnC -.maximize");
}
}
What does the program print?
Answer:
explore: :maximize
Question 149.
Consider the following Program:
public class Increase
{
public static void main(String args [ ])
{
int z = 0;
for (int y = 0; y < 100; y++)
z = z++;
System, out.println(z);
}
}
What does the Program print?
Answer:
0
Question 150.
Can you provide a declaration for a variable z such that the loop:
while (z != z + 0)
{ }
becomes an infinite loop (note that you are not allowed to declare z to be of type double or float)?
Answer:
z can be initialized to any value of type String:
String z = “BECOME YOURSELF ALWAYS!”;
The integer value 0 is converted to the string value “0” and appended to z. The resulting string is not equal to the original as computed by the equals() method; so, it can’t be surely identical, as computed by the == operator. Whence, the boolean expression:
(z != z + 0)
evaluates to true always and the loop never terminates.
Question 151.
Consider the following Program:
public class Indecision
{
public static void main(String args [])
}
System.out.println(indecisive( ));
}
static boolean indecisive( )
{
try
{
return false;
}
finally
{
return true;
}
}
}
What does the program print?
Answer:
true
Question 152.
Consider the following Program:
public class World
{
public static void main(String args [ ])
{
try
{
System.out.println(" Bye");
System.exit(0);
}
finally
{
System.out.println("Arunesh");
}
}
}
What does the Program print?
Answer:
Bye
Question 153.
Consider the following Program:
public class World
{
public static void main(String args [ ])
{
((null) null).Bye( );
}
public static void Bye( )
{
System.out.println("Arunesh");
}
}
What does the Program print?
Answer:
Arunesh
Question 154.
Consider the following Program:
public class World
{
public static void main(String args [ ])
{
System.out.println(Bye.Arunesh.Hello);
}
}
class Bye
{
static class Arunesh
{
static String Hello = "Arunesh";
}
static Z Arunesh = new Aruneshi);
}
class Z
{
String Hello = "Bye";
}
What does the Program print?
Answer:
Bye
Question 155.
Consider the following Program:
class World
{
public static final String ITEM = "10,000";
}
public class Hello extends World
{
public static final String ITEM - "1";
public static void main(String arg[ ])
{
The system, out.println (Hello. ITEM);
}
}
What does the Program print?
Answer:
1
Q. 156
Consider the following code:
for (int y = 0, int z = 0; y < 10; y++) { }
Will the code compile?
Answer:
No! You can declare the data type of at most one variable in the initialization section of the ‘for’ loop. The correct statement is:- for (int y – 0, z = 0; y < 10; y ++) { }
Question 157.
Consider the following Program:
class Hello
{
public static void main(String args[ ])
{
boolean b = 1;
System.out.println(b);
}
}
Will this program compile?
Answer:
No! Boolean variables can only take the values – true, false!!
Question 158.
Consider the following Program:
class Hello
{
public static void mainfString args[ ])
{
System.out.println(args[3]);
}
}
What does the Program print when run with the following command line?
java Hello VERY GOOD MORNING
- Hello
- VERY
- GOOD
- MORNING
- exception raised:java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:3
Answer:
Unlike C/C++, java doesn’t start the parameter count with the program name. It does however start with zero. So, in this case, zero starts with VERY, GOOD would be l, MORNING would be 2 and there is no parameter 3; hence, an exception would be raised, and thus, the correct answer is:-
5. exception raised:javadang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:3
Question 159.
Which of the following statements is true?
- Methods cannot be overridden to be more private.
- static methods cannot be overloaded.
- Private methods cannot be overloaded.
- An overloaded method cannot throw exceptions which are not checked in the super/ base class.
Answer:
- Methods cannot be overridden to be more private.
Question 160.
Consider the following Program:
class base { }
class sub1 extends base { }
class sub2 extends base { }
public class cexcp
{
public static void main(String args[ ]>
{
base b = new base( );
sub1 s1 = (sub1) b;
}
}
What zoill happen if this program is compiled and executed?
- Compile and run without any error
- Compile-time exception is raised
- The run-time exception is raised
Answer:
3. Run-time exception is raised.
Question 161.
Consider the following Program:
class base
{
public void a_mthd(int z) { }
}
public class scope extends base
{
public static void main(String args[ ])
{
}
// Method HERE
}
Which of the following methods can be legally inserted in place of the comment //Method HERE?
- void a_mthd(int z) throws Exception { }
- void a_mthd(long z) throws Exception { }
- void a_mthd(long z){ }
- public void a_mthd(int z) throws Exception { }
Answer:
2. void a_mthd(long z) throws Exception { }
3. void a_mthd(long z) { }
Question 162.
Consider the following Program:
public class Hello
{
public static void main(String args[ ])
{
/* Modifier at ZZ */ class InnerHello { }
}
}
What modifiers would be legal at ZZ in this program?
- public
- private
- static
- friend
Answer:
- public;
- private &
- static.
Question 163.
You need to create a class that will store unique object elements. You do not need to sort these elements but they must be unique.
What interface might be most suitable to satisfy this need?
- List
- Set
- Map
- Vector
Answer:
2. Set
Question 164.
Describe a java source file.
Answer:
A java source file must have “.java” extension. Also, it should have at least one top level public class definition and any number of non-public class definitions. The file name (without the extension) must match the public class name.
Question 165.
What is Bytecode?
Answer:
Every java program is converted into one or more class files. The content of each class file is a set of instructions referred to as Bytecode to be executed by the JVM. Java introduces Bytecode to produce platform independent program/code.
Question 166.
Why does the main method need a static identifier?
Answer:
The main method needs a static identifier since static methods and members do not require an instance of their class to invoke them and main is the first method that is called/’ invoked.
Question 167.
Will the program compile if the main method doesn’t have the static identifier?
Answer:
The program will still compile; but it can’t be executed or run.
Question 168.
Which is the default parent class for a Java class?
Answer:
java.lang.Object. By default, all java classes extend java.lang.Object unless they have their own parent class. Moreover, the package named java.lang is imported (by default) into all java files.
Question 169.
How are java objects passed to a method?
Answer:
Java passes both the primitive types and objects by value. During object passing, the object’s reference is copied.
Question 170.
What are native methods?
Answer:
Native methods are methods implemented in some other programming language such as C/C++. The Java Native Interface (JNI) is the API to invoke these native methods from a class in java.
Question 171.
What is the order of declaring class, package and import statements within a java.
file?
Answer:
The order should be the following:-
- package
- import statements
- class definition
Question 172.
Can a variable be an unsigned integer?
Answer:
No! Not at all!!
In java, all data types are signed numeric numbers.
Question 173.
Can a private method be static?
Answer:
YES!
A private method can indeed be static.
Question 174.
Enumerate and elucidate the various bit wise operators.
Answer:
The various bit wise operators are:-
- ∼a complement
- a&b bitwise AND
- a | b bit wise OR
- a Λ b bit wise exclusive OR (XOR)
- a<<n left shift n places
- a>>n right shift n places
- a>>>n ussigned right shift n places
Question 175.
Explain the use of ‘instanceof’ operator.
Answer:
The ‘instanceof’ operator verifies whether its first operand is an instance of its second operand.
Op1 instance of Op2 (Op1 must be the name of an object and Op2 must be the name of a class/interface/array type)
An object is considered to be an instance of a class if that object descends from that class directly/indirectly.
Example
Code:
class X
{ }
class Y extends class X
{ }
X x = new Y( );
if (x instance of X)
{
System.out.println("Instance of X");
}
if (x instance of Y)
{
System. out.println("Instance of Y");
}
Output:
An instance of X
Instance of Y
Question 176.
What are the access modifiers available for a class, method, and variable?
Answer:
public, private, protected, and default access.
Question 177.
Elucidate widening and narrowing conversions.
Answer:
A widening conversion occurs when we try to cast an object of lesser size to an object of larger size, e.g. short to long. A narrowing conversion, on the other hand, occurs when we try to cast an object of larger size to an object of lesser size, e.g. long to short.
Question 178.
How do you create Java API documentation?
Answer:
Java API documentation can be created using the javadoc utility which parses the declarations and documentation comments in a set of Java source files and produces a corresponding set of HTML pages describing (by default) the public and protected classes, nested classes (but not anonymous inner classes), interfaces, constructors, methods, and fields.
Question 179.
Explain the concept of jar, war and ear files.
Answer:
jar is Java Archive File used to package classes, property files etc. as a single file. To create a jar file we can use the Jar command just like the zip command in windows, e.g. to create a jar file with all class files under the current directory, we can use:-
jar -cvf jarfilenatne.jar *.class
war is a Web Archive File used to package a web application, i.e. classes, JSP’s, property files etc. as a single file.
ear is an Enterprise Archive File. This format is used to package EJB, JSP, Servlets, property files etc. It is generally used to package an entire enterprise application. It can consist of multiple war files.
Each war and ear will have its own deployment descriptor which is a XML based file.
Question 180.
How many JVM’s can run on a single machine?
Answer:
A JVM is like any other process. Whence, there is no limit on the number of JVM’s which can run on a single machine.,
Question 181.
Explain the Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler.
Answer:
The Java interpreter on any platform will interpret the compiled bytecode into instructions understandable by the particular hardware. However, the JVM handles one bytecode instruction at a time. The java JIT (Just-In-Time) compiler compiles the bytecode into the particular machine code as if the program had been compiled initially on that platform. Once the code has been (re)-compiled by the JIT compiler, it will, in general, run more quickly on that system.
Question 182.
Can you retrieve Java code from Bytecode?
Answer:
YES!
Class files can be decompiled using utilities such as JAD, which takes the class file as an input and generates a java file. This feature comes especially handy when you are confused as to which version of the java file was used to generate the class file in a multi-user environment.
Question 183.
Explain the concept of garbage collector.
Answer:
When an object is no longer required and its reference count is zero, it needs to be cleaned up and freed. The garbage collector does exactly this.
In fact, the garbage collector is a thread running as a part of the JVM process. This thread scans the ‘ program for objects that will never again be accessed and releases their resources back to the system. The basic garbage collector uses the mark and sweep algorithm (which marks all the unused variables whose reference count is zero and sweeps them).
Question 184.
Can you force the garbage collector to run?
Answer:
NO!
There is no way that guarantees that the garbage collector will indeed run. It runs as and when appropriate.
Question 185.
Bring out the difference between:
- String si = new StnngCxyz”);
- String s2 = “xyz”;
Answer:
“xyz” is known as a string literal.
In the first case, a new memory space is allocated in the heap on account of the ‘new’ and also allocated in the string pool on account of the literal “xyz” * In the second case, when the statement is being compiled, a pointer to the string literal “xyz”
is stored in s2.
Question 186.
When intern( ) method on a String object is invoked, what happens?
Answer:
Interned strings avoid duplicate strings. There is only one copy of each String that has been interned, no matter how many references point to it. The process of converting duplicated strings to shared ones is called interning and is accomplished by means of the intern( ) method.
Question 187.
Bring out the purpose of the StringTokenizer class.
Answer:
The StringTokenizer class allows an application to break a string into tokens. The StringTokenizer methods do not distinguish between identifiers, numbers, and quoted strings, nor do they recognize and skip comments. The set of delimiters (the characters which separate tokens, one from the other) can be specified either at creation time or on a pre-token basis.
Example
Code:
StringTokenizer strtok = new StringTokenizer ("Testing IT OUT!");
while (sfrfok.hasMoreTokens( )
{
System.out.println(strtok.nextToken( ));
}
Output:
Testing
IT
OUT!
Question 188.
Which collection sorts data?
Answer:
TreeMap.
Question 189.
Bring out the difference between Hashtable and HashMap.
Answer:
The main point of difference between Hashtable and HashMap is that while in a Hashtable, methods are synchronized and thus thread safe, in a HashMap, methods are not synchronized, not thread safe, making it faster.
Question 190.
Bring out the difference between Enumeration and Iterator interface.
Answer:
The main point of difference between Iterators and Enumerations is that Iterators allow the caller to remove elements from the underlying collection during the iteration but Enumerations do not allow any such provision.
Question 191.
What do you understand by the Throwable class?
Answer:
The Throwable class is the superclass of all errors/exceptions in the Java language so that only objects that are instances of the Throwable class or one of its subclasses are thrown by the JVM. Thus, only the Throwable class or one of its subclasses can be the argument type in a catch clause.
Question 192.
How can you write your own customized exceptions?
Answer:
Customized exceptions can be written by extending the java.lang. Exception class. In this context, it would be worthwhile to mention that the toString( ) method should be overridden to print an appropriate error message.
Question 193.
Suppose an exception goes uncaught; what happens in such a case?
Answer:
An uncaught exception results in the uncaughtException( ) method of the thread’s ThreadGroup being called, which ultimately causes the termination of the program in which it is thrown.
Question 194.
What gets printed when the printStackTrace( ) method is invoked?
Answer:
public void printStackTrace( )
Prints this.throwable and its backtrace to the standard error stream. This method prints a stack trace for this Throwable object on the error output stream that is the value of the field System.err. The first line of this output contains the result of the toString( ) method for this object while the remaining lines represent data previously recorded by the filllnStackTrace( ) method.
The exact format of all this information is implementation dependent but the following may be regarded as a typical case:-
java.lang.NullPointerException
at Cls.muchjCls.java: 9)
at Cls.lunch(Cls.java: 6)
at Cls.main(Cls.java: 3)
The above output was produced by executing the following program:-
class Cls
{
public static void main(string args[ ])
{
lunch(null);
}
static void lunch(int [ ] x)
{
much(x);
}
static void lunch(int [ ] y)
{
System.out.println(y[0]);
}
}
Question 195.
How do you use these ( ) and super( ) methods with constructors? Bring out the difference between their use.
Answer:
this( ) method within a constructor is used to invoke another constructor in the same class while the super( ) method within a constructor is used to invoke its immediate superclass constructor.
Question 196.
Does java support operator overload?
Answer:
No! Not at all!!
However, java internally supports operator overloading in the form of performing String concatenation using the ‘+’ operator.
Question 197.
Compare and contrast Interfaces with Abstract classes.
Answer:
In this context, consider the following main points:-
(1) Neither interfaces nor abstract classes can be instantiated.
(2) Direct multiple inheritance is not allowed in Java unlike C++. But, java provides for interfaces to take care of this problem. A class can implement any number of interfaces, but can extend only one class.
(3) An interface has all public members and no implementation whatsoever. An abstract class is a class which may have the usual features of class members such as private, protected etc. but has some abstract methods.
(4) Interfaces should be used as much as possible and an abstract class must be used only when you want to provide some but not complete implementation.
Question 198.
Can you instantiate an abstract class? Elaborate.
Answer:
As mentioned in the previous problem, we cannot instantiate an abstract class. In order to declare an abstract class, we use the modifier or keyword abstract before the class keyword in our class definition, e.g.
abstract public class Form
{
.....................
.....................
}
class Circle extends Form
{ }
If you try to create an instance of the abstract class Form, the compiler reports an error!
Question 199
Can you declare an abstract class as final? If not, why not?
Answer:
An abstract class cannot be declared as final.
The purpose of having an abstract class is that its subclasses can extend its functionality and this very purpose of declaring an abstract class will be defeated in case an abstract class is allowed to be declared as final.
Question 200.
Bring out the use of the ‘transient’ keyword. ,
Answer:
On Object Serialization, if any of the object’s members need not be serialized, they must be declared as transient.