100 java interview questions: In this tutorial, we have discussed the Top 100+ Core Java Interview Questions and Answers for fresher. This article helps you to understand the basic concept of Java programming for interview purposes. All the Java concepts are explained here with an example for better understanding. This article covers Java topics like Java basic concept, Java OOPs concept, Java Multithreading, Java Collection, Java Serialization, Java Exception Handling, etc.
- Java Basics Interview Questions and Answers
- Java OOPs Interview Questions and Answers
- Java String Handling Interview Questions and Answers
- Exception Handling Interview Questions and Answers
- Java Multithreading Interview Questions and Answers
- Java Collection Interview Questions and Answers
- Java Serialization Interview Questions and Answers
Java Basics Interview Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is Java?
Answer
Java is an Object-Oriented, platform-independent, robust, and high-level programming language. It was developed by James Gosling, Patrick Naughton, Chris Warth, Ed Frank, and Mike Sheridan at Sun Microsystem in 1991. We can make the Desktop application, Web application, Enterprise application, Mobile application, and Games with the help of Java.
Question 2.
What are the various features in Java?
Answer
- Object-Oriented: Java is an Object-Oriented programming language that allows you to maintain your code with the help of objects.
- Platform-Independent: Java is platform-independent that means single Java programs work on different platforms without any changes.
- Robust: Java is a robust programming language that uses strong memory management. A concept like automatic garbage collection, exception handling makes it more robust.
- Multithreaded: Java supports a multithreaded programming approach that deals with many tasks at once by creating multiple threads.
- High performance: Java bytecodes enable high performance in Java.
Question 3.
What is JVM?
Answer
JVM stands for Java Virtual Machine. JVM enables the computer to run the program. It provides the runtime environment in which Java bytecodes can be executed. JVM is platform-dependent i.e. for each software and hardware we have different JVM configurations. JVM doesn’t exist physically. It is abstract in nature.
Question 4.
What is the JIT compiler?
Answer
Jit compiler stands for the Just-in-Time compiler. The JIT compiler is an essential part of JRE(Java Runtime Environment). The JIT compiler is used to improve the performance. The JIT compiler compiled the code when it is needed, not before runtime, and hence reduces the amount of time needed for compilation.
Question 5.
What is the difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM?
Answer
JVM: JVM stands for Java Virtual Machine. JVM enables the computer to run the program. It provides the runtime environment in which Java bytecodes can be executed. JVM is platform-dependent i.e. for each software and hardware we have different JVM configurations. JVM doesn’t exist physically. It is abstract in nature.
JRE: JRE stands for Java Runtime Environment. It contains a JVM + set of Libraries. JRE contains the set of Libraries that JVM uses at runtime. JRE is the minimum requirement to run any Java code. JRE physically exists and platform dependent.
JDK: JDK stands for Java Development Kit. It contains JRE + development tools. JRE contains a JVM + set of Libraries and Development tools comprised of Debugger + Compiler + JavaDoc. You can say that JDK is a complete package for any Java application development. You can run your code, execute your code, launch your application with the help of JDK.
Question 6.
Explain why Java’s main method is public static void main(String args[])?
Answer
public: the public is an access specifier that can be used to specify who can access this method. JVM calls the main method from outside the class, therefore, it is necessary to make Java’s main method public.
static: static is a keyword in Java. We can make a static variable and static method in Java with the help of a static keyword. The main advantage of the static method is we can call the method without creating an instance of a class. JVM calls the main method without creating an instance of a class, therefore it is a must to make the main method is static.
void: void is a return type of a method that indicates void defines the method which will not return any value.
main: main is the name of the method. This is the name that is configured inside the JVM. It is the method where the main execution starts.
String args[]: String in Java is a class that is used to store Strings, and args is a reference variable that refers to an array of String types. If you want to pass the argument through a command line then it is a must-make main method String args[].
Question 7.
Why Java is a platform-independent language?
Answer
As we know, when we compile Java code it internally converted into bytecode which can run on any machine irrespective of its underlying operating system. That’s why Java is a platform-independent language.
Do Refer:
- Java Programming Language Tutorial
- What is Collection Framework in Java?
- Statement Interface in Java
Question 8.
Why Java is not a 100% Object Oriented programming language?
Answer
Java is not a 100% Object Oriented Programming language because of its primitive data types such as int, byte, long, short, etc. which are not objects. The static keyword is another reason which doesn’t make Java a 100% Object Oriented Programming language, As we know we can access a static variable or static function without creating the instance of a class.
Question 9.
What are the various access modifiers available in Java?
Answer
Access modifiers in Java is a special keyword that is used to restrict the access of a class, member variable, constructor, and function into another class.
There are 4 types of access specifier available in Java:
- Public: The methods, variables, and classes that are defined as the public can be accessed by the same class or outside the class or the same package as well as outside the package.
- Protected: protected modifier can be accessed from any class of the same package and a child class from another package.
- Default: default can be accessed only from the class of the same package.
- Private: private methods, variables, and classes can be accessed from the same class in which they are declared, they cannot be accessed from outside the class body.
Question 10.
How many types of variables in Java?
Answer
There are three types of variables are used in Java:
1. Local Variable: The Local variable is declared inside the body of the method. We can use a local variable only within a method. The main advantage of the local variable is that the other method in the class would not be even aware of that variable.
2. Instance Variable: The instance variable is declared inside the class but outside the method body. The value of the instance variable is instance specific and it is not shared among other instances.
3. Static Variable: The variable which is declared as static is known as a static variable. We can have only one copy of the static variable and shared it among all the instances.
Question 11.
Why pointers are not used in Java?
Answer
The pointers are not used in Java because pointers are unsafe, it increases the complexity of the program. Java uses the reference type to hide pointers and programmers feel easier to deal with reference type without pointers.
Question 12.
What is the difference between the break and continue statement?
Answer
The break statement exits the loop and executes the statement after the loop whereas the current statement skips the current iteration and jumps to the next iteration.
Question 13.
What is the classloader in Java?
Answer
The classloader in Java is used to load a class file. Whenever JVM runs a java program it is loaded first by the classloader. The ClassLoader class uses a delegation model to search for classes and resources.
Question 14.
What are packages in Java?
Answer
Packages are nothing more than the way we organize files into different directories according to their functionality, usability as well as the category they should belong to.
for example files in the java.io package do something related to I/O, but files in java.net give us the way to deal with the network
Question 15.
What are the advantages of a package in Java?
Answer
- The package also helps us to avoid class name collision when we use the same class name as that of others.
- The package reflects the ease of maintenance, organization, and increase collaboration among developers.
Java OOPs Interview Questions and Answers
Question 16.
What is the Object-Oriented Paradigm?
Answer
It is a programming style that is associated with the concept of object and class and another concept like Inheritance, Polymorphism, Abstraction, Encapsulation, etc. The main advantage of the Object-Oriented paradigm is code reusability.
Question 17.
What is a Java Class?
Answer
The class is the core of Java. It is the logical entity upon which the entire Java language is built because it defines the shape and nature of an object. As such the class is an important part of object-oriented programming in Java. The most important thing to understand about a class is that it is used to defines a new data type. Once we defined, this new data type can be used to create objects of that type.
Question 18.
What is an Object?
Answer
The Object is an entity that has a state and behavior. The object is an instance of a class and an object is a real-world entity. To access the members who are defined in the class you need to create an object.
for example, a chair, pen, table, bike, book, etc are the example of Object.
Question 19.
What is the singleton class in Java?
Answer
The singleton class is a class that allows you to create only one object. It saves lots of memory because the object is not created at each request. We can create a singleton class by making its constructor private.
Question 20.
What is Inheritance in Java?
Answer
Inheritance is one of the key features of object-oriented programming (OOPs). Inheritance is a process of inheriting the properties and behavior of the existing class into a new class. When we inherit the class from an existing class, we can reuse the methods and fields of the parent class. Inheritance can be defined as the Is-A relationship, which is also known as the parent-child relationship.
Question 21.
Why we use Inheritance in Java?
Answer
There are two main reasons to use Inheritance in Java:
- The main purpose of inheritance is code reusability. We can reuse the code when we inherit the properties and behavior of the existing class into a new class.
- The runtime polymorphism (method overriding) can be achieved by inheritance.
Question 22.
What are the different types of Inheritance in Java?
Answer
Java supports only three types of inheritance Single Inheritance, Multilevel Inheritance, and Hierarchical Inheritance. Multiple and Hybrid Inheritance in java can be supported through interface only.
- Single Inheritance: In single inheritance, one class can extend the functionality of another class. In single inheritance only one parent and one child class is present.
- Multilevel Inheritance: In multilevel inheritance, there is more than one level. If one class can inherit from a derived class and the derived class becomes the base class of the new class then it is called multilevel inheritance.
- Hierarchical Inheritance: In Hierarchical inheritance, from a single parent class, we are inheriting multiple child classes.
Question 23.
Why Java doesn’t support Multiple Inheritance?
Answer
Java doesn’t support multiple inheritances due to the ambiguity problem.
Consider a scenario where X, Y, and Z are the three classes. The Z class inherits both the class i.e. class X and class Y. If class X and class Y have the same method and we call it from child class object ( class Z object), there will be ambiguity to call the method of class X or a class Y. Therefore compiler show compiles time error if we inherit 2 classes.
Question 24.
What is polymorphism in Java?
Answer
Polymorphism in Java is a concept which allows you to perform a single action in different ways. It is the ability of an object or method to take different forms as per requirements. Polymorphism is one of the most important features of object-oriented programming (OOPs). Polymorphism is a combination of 2 Greek words: poly and morph. The poly word means many and morphs words mean forms. So when one thing has many forms it is known as polymorphism.
Consider a scenario where Car is a class that has a method speed(). However, the speed of the car may different according to cars. for example, the Maruti car has a speed of 60 Km/h, the Alto car has a speed of 70 km/h, and the Brezza car has a speed of 80 km/h. So here is a single method called speed() but their behavior is different according to cars. This is called polymorphism in Java.
Question 25.
What are the different types of polymorphism in Java?
Answer
There are two types of polymorphism in Java:
- Static Polymorphism.
- Dynamic Polymorphism.
Compile-time polymorphism is also known as static polymorphism and runtime polymorphism is also known as dynamic polymorphism. Method Overloading is a way to implement compile-time polymorphism and the Method Overriding is a way to implement runtime polymorphism.
Question 26.
How many ways to overload a method?
Answer
There are three ways to overload a method in Java.
- By changing the number of parameters.
- By changing the data type.
- By changing the sequence of the data type.
Question 27.
What is the difference between Method Overloading and Method Overriding in Java?
Answer
- Overloading happens at compile-time whereas Overriding happens at runtime.
- Overloading is done in the same class whereas Overriding inheritance is required.
- In overloading, the parameter must be different while in overriding the parameter must be the same.
- The main purpose of overloading is to increase the readability of the program while overriding the class gives its own implementation to an inherited method without even modifying the parent class code.
- Private, static, and final methods can be overloaded but cannot be overridden.
- The return type can be the same or different in overloading while the overriding return type must be the same or covariant return type.
- Overloading is also known as compile-time polymorphism or static polymorphism or early binding while overriding is also known as runtime polymorphism or dynamic polymorphism or late binding.
Question 28.
What is Encapsulation in Java?
Answer
Encapsulation is an act of combining properties and methods of the same entity. In other words, it is a process of wrapping the data (variables) and code together in a single unit. A capsule is an example of encapsulation which is mixed of several medicines.
Question 29.
What are the advantages of Encapsulation in Java?
Answer
- Encapsulation is a way to achieve the data hiding in java so that the other class will not be able to access the private members of the class.
- In Encapsulation, we can hide the internal information of the data which is better for security concerns.
- With Java Encapsulation, we can make the class read-only i.e. A class that has only getter methods, and write-only i.e. A class that has only setter methods. If we don’t want to change the value of a variable, we can use the read-only class. If we want to change the value of a variable, we can use the write-only class.
- In Encapsulation, we can combine the variables and methods in a single unit. So that the encapsulation provides control over the data.
Question 30.
How we can achieve Encapsulation in Java?
Answer
In Java, we can achieve encapsulation by declaring all the data members (variables) of the class private. If the data member is private then it can be only accessible within the same class. No other class can access the data member of that class. Now the question arises if we are declaring all the data members (variables) of the class private then how should we use this data member. So the answer is we can use the setter and getter method to set and get the value of data member (variable) of the class private.
Question 31.
What is an abstraction in Java?
Answer
Abstraction in Java is an essential element of Object-Oriented Programming and it is the process of hiding the implementation details and showing only functionality to the user.
Question 32.
How we can achieve abstraction in Java?
Answer:
There are two ways to achieve abstraction in Java.
- abstract class (achieve 0-100%)
- interface (achieve 100%)
Question 33.
What is the abstract class in Java?
Answer:
A class that is declared abstract with the help of abstract keywords is known as an abstract class in Java. An abstract class is a way to achieve abstraction in Java( but not 100%). We cannot create the instance of an abstract class but we can create a reference of an abstract class.
Question 34.
What is the abstract method in Java?
Answer:
A method that is declared abstract with the help of abstract keyword is known as the abstract method in Java. The Abstract method doesn’t have method implementation, it only has a method signature. The abstract method must be declared and created inside the abstract class.
Question 35.
What is a constructor?
Answer:
The Constructor is a member function of a class. The name of the constructor is the same as the name of the class. It doesn’t return any value. Whenever we are creating an instance of the class using the new keyword by default a constructor is called implicitly known as the default constructor. It initializes the newly created object.
Question 36.
What are the different types of Constructors in Java?
Answer:
There are two types of constructors in Java.
i) Default Constructor: When there is no constructor defined in the class by the programmer, the java compiler implicitly provides a default constructor for the class. This constructor is known as the default constructor in java. It doesn’t accept any parameter. If we create any constructor in our class then the java compiler doesn’t create any constructor in our class.
ii) Parameterized Constructor: A constructor that accepts one or more parameters is known as a parameterized constructor. Whenever we have to create an object of the class that has a parameterized constructor, we need to pass the arguments so that this constructor gets invoked after the created object.
Question 37.
What is Constructor Overloading in Java?
Answer:
Constructor overloading is just like method overloading. When more than one constructor is defined in a class with a different parameter list, then it is called constructor overloading in java or the use of multiple constructors in a class. In constructor overloading, every constructor performs a different task.
Question 38.
What do you mean by Constructor Chaining?
Answer:
Constructor Chaining is a process in which a Constructor can call other Constructor of the same class or superclass. The Constructor call from a constructor must be the first step (first line). The first line of the constructor is either super() or this(), super() keyword is used to call the superclass constructor and this() keyword is used to call the same class constructor. The process of Constructor chaining can be achieved through inheritance only.
Question 39.
What is Java Copy Constructor?
Answer:
Copy Constructor is a constructor that is used to create a copy of an already existing object of the same class. It takes a single argument whose type is that of the class containing constructor. Unlike C++, there is no copy constructor in java. But we can copy the value of one object into another in java by a constructor, assigning the value of one object into another, and by object cloning (clone() method of object class).
Question 40.
What are the differences between the Constructor and Method?
Answer:
The differences between Constructor and Methos are given below:
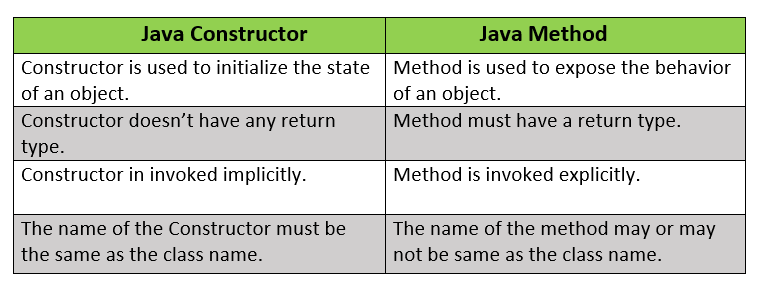 Question 41.
Question 41.
What are the differences between this and super keyword?
Answer:
this is a reference variable that is used to refer to the current class object. this can also be used to invoke a current class method. This () can be used to invoke the same class constructor.
The super is a reference variable in Java that is used to refer to the immediate parent class object. The super can also be used to invoke the immediate parent class method. The super() is used to invoke the parent class constructor.
Question 42.
What is the interface in Java?
Answer:
The interface is a blueprint of a class. Like class interface have variables and methods but the methods declared inside the interface are by default abstract. We can declare an interface with the help of an interface keyword. Every method present inside the interface is public and abstract whether we are declaring or not.
Question 43.
Why we use interface in Java?
Answer:
- To achieve 100% abstraction.
- By interface, we can achieve multiple inheritances in Java.
Question 44.
What are the differences between an interface and an abstract class?
Answer:
The interface and abstract classes both are used to achieve abstraction in Java. But there are few differences between them which are given below.
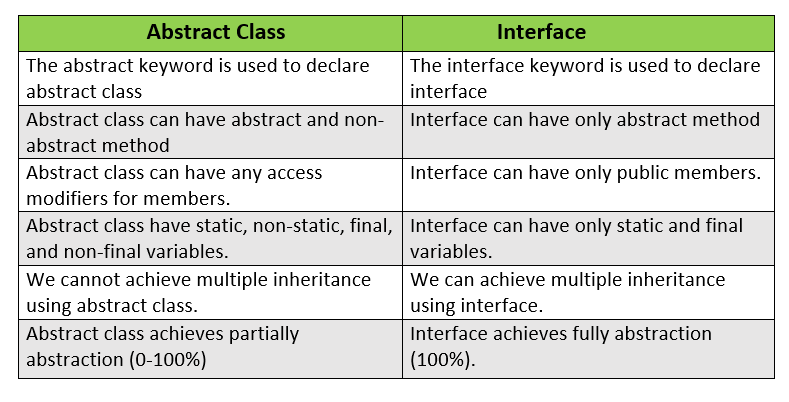 Question 45.
Question 45.
What is the wrapper class?
Answer:
Wrapper class provides a mechanism to convert primitive data types into an object and vice-versa.
Question 46.
What is autoboxing?
Answer:
Autoboxing in Java is a mechanism to convert primitive data types into an object of their corresponding wrapper class.
Question 47.
What is unboxing?
Answer:
Unboxing in Java is the reverse process of autoboxing. The unboxing is a mechanism to convert an object of a wrapper class to its corresponding primitive data type.
Java String Handling Interview Questions and Answers
Question 48.
What is the String pool in Java?
Answer:
String pool in Java is a space reserved in the heap memory which can be used to store String. Whenever we created a new object, the string pool first checks whether the object is present in the string pool or not. If it is already present then the same reference is returned otherwise a new object will be created in the string pool and then return the reference.
Question 49.
Why String is immutable in nature?
Answer:
The meaning of the immutable string is once we create a string its value cannot be changed. The String is immutable in nature because it uses the concept of String literals. Let’s take an example to understand this
String s1 = “Java”;
String s2 = “Java”;
In this example, the two reference variable refers to the same object. if one reference variable changes the value of the object (suppose “java” to “python”), It will affect all the reference variables. That’s why String is immutable in nature.
Question 50.
How many ways to create a String in Java?
Answer:
There are two ways to create a String in Java:
i) By using String literals: Java String with the help of String literal is created using the double-quotes.
String s = “Javastudypoint”;
Each time when you create a String using String literal, the JVM first checks whether the object is present in the string pool or not. If it is already present then the same reference is returned otherwise a new object will be created in the string pool and then return the reference.
ii) By using the new keyword: When we create a String using the new keyword, the JVM creates a new String object in heap memory, and the String literal “Javastudypoint” will be placed inside the String pool and the variable str will refer to the String object in heap.
String str = new String(“Javastudypoint”);
Question 51.
What are the differences between “== operator” and “equals() method”?
Answer:
The “== operator” in String is used for reference comparison whereas the equals() method is used for content comparison.
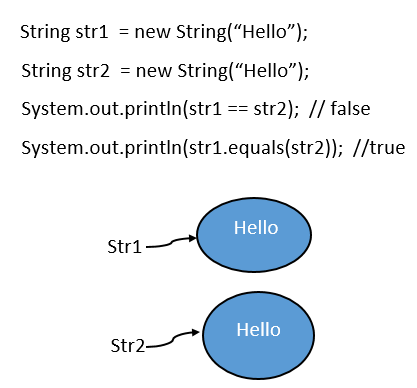
In the above example, both the reference variable(str1 & str2) contain the same String but their references are not the same, therefore “== operator” returns false and equals() method return true.
Question 52.
What are the differences between String and StringBuffer?
Answer:
The differences between String and StringBuffer is given below:
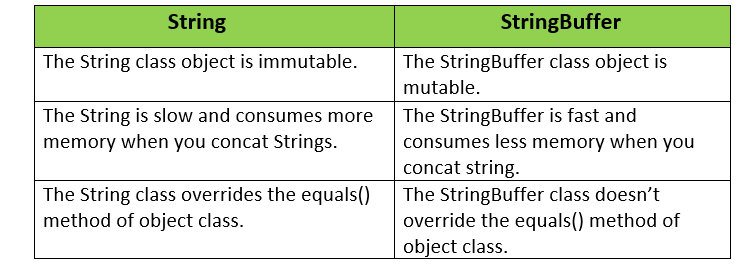
Question 53.
What are the differences between StringBuffer and StringBuilder?
Answer:
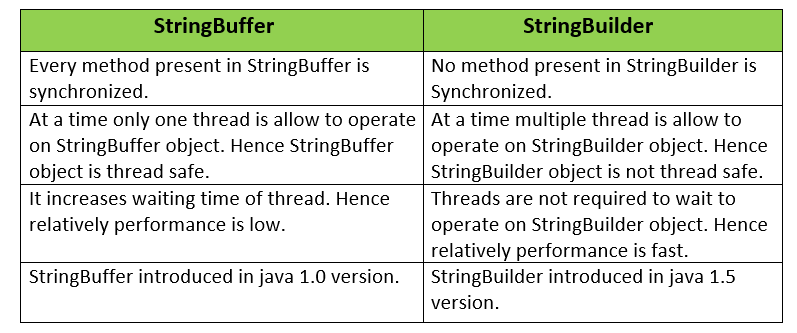
The differences between StringBuffer and StringBuilder is given below:
Exception Handling Interview Questions and Answers
Question 54.
What is Exception Handling in Java?
Answer:
Exception Handling in Java is a mechanism that allows you to handle runtime errors so that the normal flow of the program can be maintained. Suppose If an exception occurs in your code (suppose in line 6), then the rest of the code is not executed. Therefore Java compiler creates an exception object and this exception object directly jumps to the default catch mechanism. Where there is a default message which is print on the screen and our program gets terminated.
Question 55.
What are the differences between Exception and Error?
Answer:
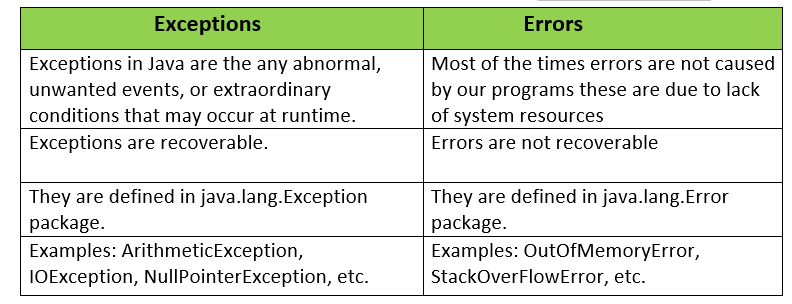
Both Exception and Error are the child classes of the java.lang.Throwable class but there are few differences between them which are given below:
Question 56.
Why an exception occurs?
Answer:
Exceptions in Java can occur due to the following reasons:
- Wrong data entered by the user.
- Network Connection problem.
- Hardware problem.
- Opening a file which is not existing in your program.
- Server down problem.
Question 57.
Explain Java Exception class hierarchy?
Answer:
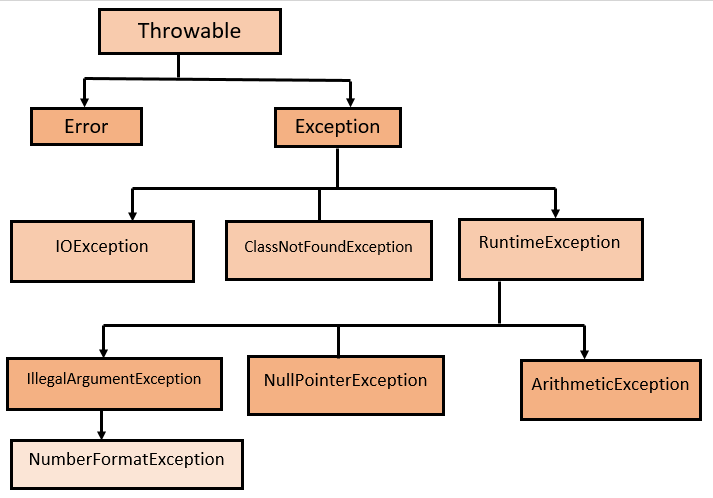
The java.lang.Throwable is the parent class of all the exceptions in Java. There are 2 child classes of Throwable class i.e. Exception and Error. The Exception class represents the exception that is handled by our programmers using the try and catch block. The Exception class hierarchy is given below:
Question 58.
What are the different types of Exception in Java?
Answer:
There are two types of exceptions in Java (Checked and Unchecked exceptions).
i) Checked Exception: All the classes which inherit throwable class except RuntimeException and Error are known as Checked Exception. The checked exceptions are checked by the compiler at compile-time. In case of checked exceptions if programmers will not handle the exception then we will get a compile-time error. We will handle the checked exception by using a try-catch block or and declare using the throws keyword.
For example, FileNotFoundException, ClassNotFoundException, IOException, SQLException etc.
ii) Unchecked Exception: All the classes which inherit RuntimeException are known as Unchecked Exception. The Unchecked exceptions are not checked by the compiler at compile-time. But they are checked at runtime. In the case of an Unchecked exception if programmers will not handle the exception then we won’t get a compile-time error.
For example, ArithmeticException, NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBounds etc.
Question 59.
Explain all the keywords used in Exception Handling?
Answer:
There are five keywords are used to handle the exception in Java. Which are given below:
- try: In the try block, we can write the code that might throw an exception.
- catch: catch block is used to handle the exception that may occur at runtime.
- finally: finally block is used for clean-up code. finally block is always run.
- throw: throw is used to throw an exception, it can throw an exception explicitly.
- throws: throws are used to declaring an exception so that the programmer is responsible to write exception handling code.
Question 60.
What are the different ways to handle the exception?
Answer:
There are two ways to handle the exception which are mentioned below:
- By using a try-catch block.
- By using the throws keyword.
Question 61.
What are the differences between throw and throws?
Answer:
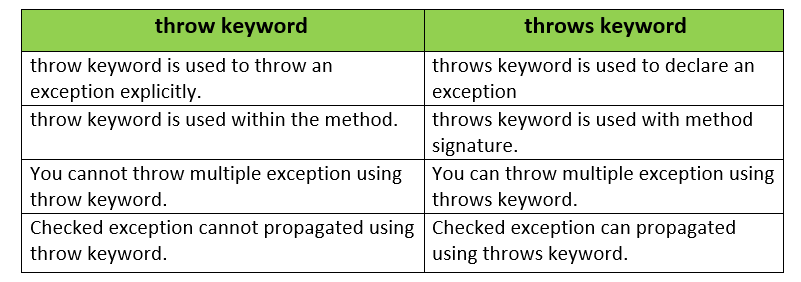
The differences between throw and throws keyword are given below:
Question 62.
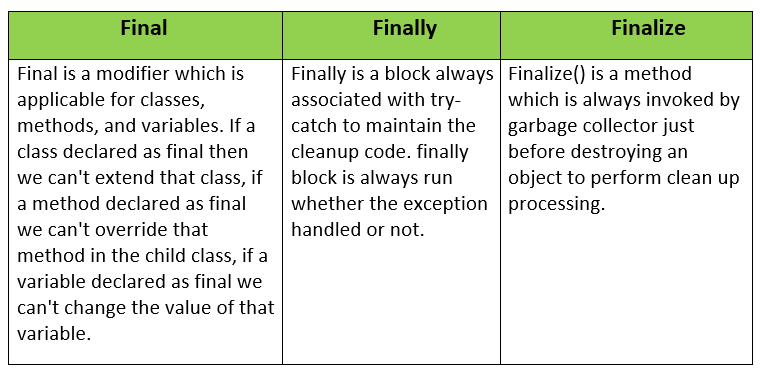
What are the differences between final, finally, and finalize?
Answer:
The differences between final, finally, and finalize are given below:
Java Multithreading Interview Questions and Answers
Question 63.
What is the thread?
Answer:
A thread is a lightweight process. A thread is an independent path of execution within a program. Many threads can run concurrently within a program.
Question 64.
What is Multithreading?
Answer:
Multithreading refers to executing multiple threads simultaneously. Multithreading is a way to obtain multitasking. The multithreaded program consumes less memory and gives a fast efficient program.
Question 65.
Why we use Multithreading in Java?
Answer:
The Multithreaded program enables you to write a very efficient program that makes maximum use of CPU because the idle time can be kept to a minimum. In a single-threaded environment, your program has to wait for each of these tasks to finish before it can proceed to the next one even though the CPU is sitting idle most of the time. Multithreading lets you gain access to this idle time and put it to good use.
Question 66.
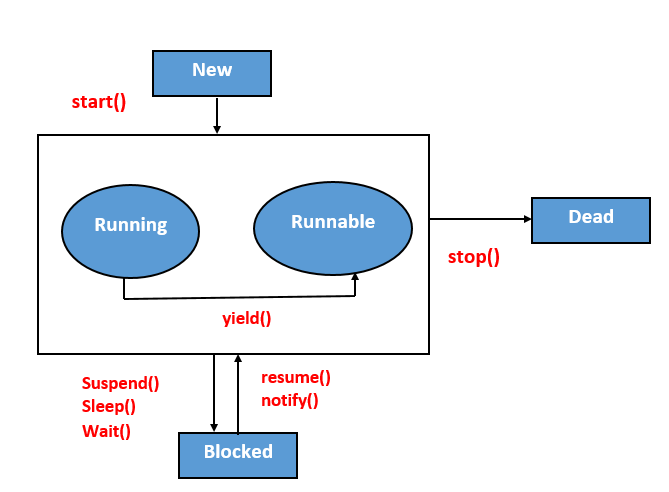
Explain all the states in the lifecycle of a thread?
Answer:
All the states of the thread life cycle are explained below:
- New: When we create a thread using thread class then the thread goes into a new state.
- Runnable: In this state, the thread is ready to run after calling the start() method of the Thread class.
- Running: The thread scheduler picks the thread from the ready state and the thread is in execution.
- Blocked: In this state, the thread is waiting for another thread to finish.
- Dead: In this state, a thread is dead when the run() method exists.
Question 67.
How many ways to create a thread in Java?
Answer:
There are two ways to create a thread in Java:
i) By extending Thread class: The first way to create a thread is to create a new class that extends the thread class, and then to create a new instance of that class. The extending class must override the run() method of the Thread class.
public class Example extends Thread{
public void run{
}
}
ii) By implementing the Runnable interface: The second way to create a thread is to create a new class that implements the Runnable interface. To implement Runnable, a class needs only implement the run() method.
public class Example implements Runnable{
public void run(){
}
}
Question 68.
Which is the better way to create a thread in Java?
Answer:
The first way to create a thread by extending a thread class. In this approach, there is no chance to extend any other class and we are missing the benefits of multiple inheritances. The second way to create a thread by implementing a Runnable interface, therefore, we can extend any other class and we are able to use the benefits of multiple inheritances. So we can say that the Runnable interface is the best way to create a thread in Java.
Question 69.
What does is the Alive() and join() method?
Answer:
The is Alive() method is used to test the thread is alive or not. It returns true if the thread is alive otherwise it returns false. On the other hand, the join() method is waiting for a thread to die. The join() method allows you to specify the maximum amount of time that you want to wait for the specified thread to terminate.
Question 70.
Difference between the wait() and sleep() methods?
Answer:
wait(): The wait() method defined in the object class and tells the calling thread to give up the monitor and go to sleep until some other thread enters the same monitor and calls notify() or notifyAll() method.
sleep(): The sleep() method defined in the Thread class. The sleep() method is used to pause the execution of a thread for a specified amount of time. When we call the sleep() method it pauses the execution of the current thread and gives the chance to another thread.
Question 71.
What is the purpose of the yield() method in java?
Answer:
Yield() method in java causes to pause the currently executing thread for giving the chance to remaining waiting threads of the same priority. Suppose in our program there is 2 thread t1 and t2. Thread t1 takes 1 hour to complete its execution while Thread t2 takes 10 minutes to complete its execution. Since Thread t1 will complete its execution after 1 hour, thread t2 has to wait for 1 hour to just finish the 10 minutes job. In such a scenario the yield() method comes into the picture. The thread scheduler pauses the currently executing thread and gives the chance to any other remaining waiting thread.
Question 72.
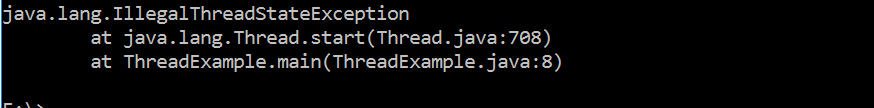
Is it possible to start a thread twice?
Answer:
No, it is not possible to start a thread twice once a thread is started and executed it goes into the dead/terminated state. Therefore if we try to start a thread twice it will throw a runtime exception IllegalThreadStateException.
Example:
class ThreadExample extends Thread{
public void run(){
System.out.println("thread is executing");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
ThreadExample t1 = new ThreadExample();
t1.start();
t1.start();
}
}
Output:
Question 73.
Differentiate between wait(), notify(), and notifyAll() method?
Answer:
- wait: The wait() method defined in the object class and tells the calling thread to give up the monitor and go to sleep until some other thread enters the same monitor and calls notify() or notifyAll() method.
- notify(): notify() method in java is used to wakes up a thread called wait() on the same object.
- notifyAll(): notifyAll() method in java is used to wakes up all the threads that called wait() on the same object.
Question 74.
What are daemon threads?
Answer:
The threads which are executing in the background are known as daemon threads. The main objective of daemon threads is to provide support for nondaemon threads(user threads). The daemon threads will automatically be terminated by the JVM when all the user threads die. We can check whether the thread is daemon or not by using is Daemon() method.
Question 75.
What is Synchronization?
Answer:
When we start two or more threads within a program, there may be a situation when multiple threads try to access the same resource. Then we need some way to ensure that the resource will be used by only one thread at a time. The process by which this is achieved is known as synchronization.
Question 76.
How we can achieve synchronization in Java?
Answer:
We can achieve synchronization in Java in three ways.
- By synchronized block.
- By synchronized method.
- By static synchronization.
Question 77.
What do you mean by suspending, resuming, and stopping the thread?
Answer:
Suspending a thread means puts the thread running to waiting for the state. The suspend() method of the Thread class is used to put the thread running to waiting for the state. The resume() method is used to resume the suspended thread. The stop() method of thread class stops the execution of the thread completely.
Question 78.
What is a thread pool?
Answer:
The thread pool is a group of fixed size threadm, creating a new thread for every job may create performance and memory problems to overcomes this problem we should go for the thread pool. The thread pool pulled out a thread and assigned a job by the service provider after the completion of this job the thread is contained in the thread pool again. By using a thread pool we can enhance the performance. We can create a thread pool by using ExecutorService.
Java Collection Interview Questions and Answers
Question 79.
What is Collection Framework in Java?
Answer:
The Collection Framework provides a well-designed set of classes and interfaces for storing and manipulating a group of data as a single unit. We can perform all the operations on data such as searching, sorting, insertion, manipulation, and deletion using the Java Collection Framework.
Question 80.
What is the need for the Collection Framework?
Answer:
Before the Collection Framework (before JDK 1.2) was introduced, the common methods for grouping java objects were Arrays. Let’s first understand the problems with Arrays.
- Arrays have a fixed size. Once we declared the size of an array, we can’t grow and shrink the size of the array
- Arrays can hold only homogenous types of elements.
- To perform operations such as sorting, searching, insertion, and deletion on an array you have to define methods.
To overcome the problems of arrays we should go for Collection Framework in Java.
- Collections are growable in nature, based on our requirements we can grow and shrink the size of the array.
- Collections can hold homogenous as well as heterogeneous elements.
- In collections, predefined methods are available for every requirement. Being a programmer we have to use this predefined method and we are not responsible to provide the implementation.
Question 81.
List out all the classes and interfaces used in the collection framework
Answer:
Interfaces: All the interfaces used in the Collection framework are given below:
- Collection
- List
- Queue
- Deque
- Set
- SortedSet
- Map
- SortedMap
Classes: All the classes used in the Collection framework are given below:
- ArrayList
- LinkedList
- Vector
- Stack
- HashSet
- LinkedHashSet
- TreeSet
- PriorityQueue
- HashMap
- LinkedHashMap
- TreeMap
- HashTable
Question 82.
What are the differences between Array and ArrayList?
Answer:
The array is a data structure. Once we create an array we cannot grow or shrink the size of an array as per need. On the other hand, the ArrayList is a class that is a part of the collection framework. We can grow or shrink the size of an ArrayList as per need.
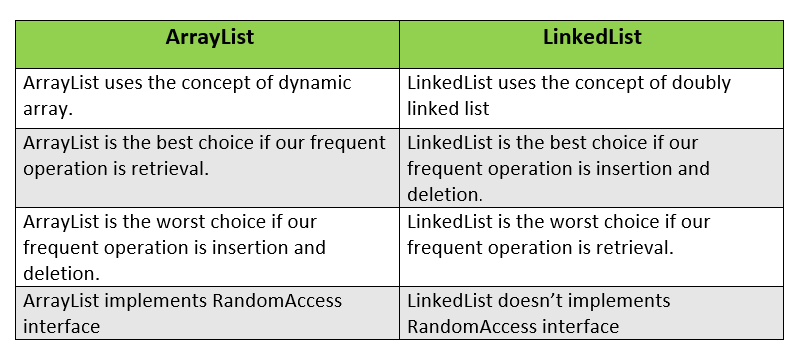
Question 83.
Difference between ArrayList and LinkedList
Answer:
The differences between ArrayList and LinkedList is given below:
Question 84.
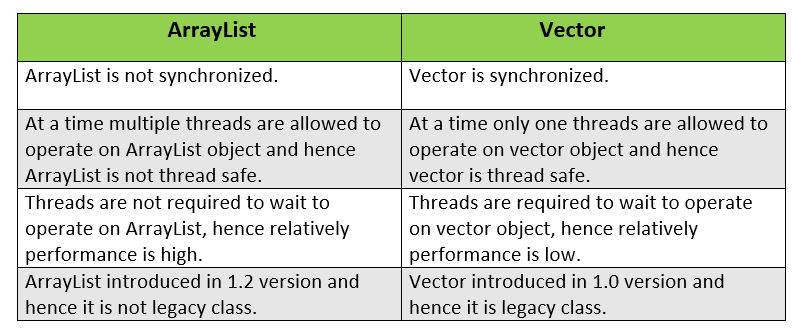
What are the differences between ArrayList and Vector?
Answer:
The differences between ArrayList and Vector is given below:
Question 85.
What are the differences between List and Set?
Answer:
The List and Set both extends the collection interface but there are few differences between them which are discussed below:
- In List, duplicates are allowed whereas in the Set duplicates are not allowed.
- The List preserves the insertion order whereas the Set insertion order doesn’t preserve.
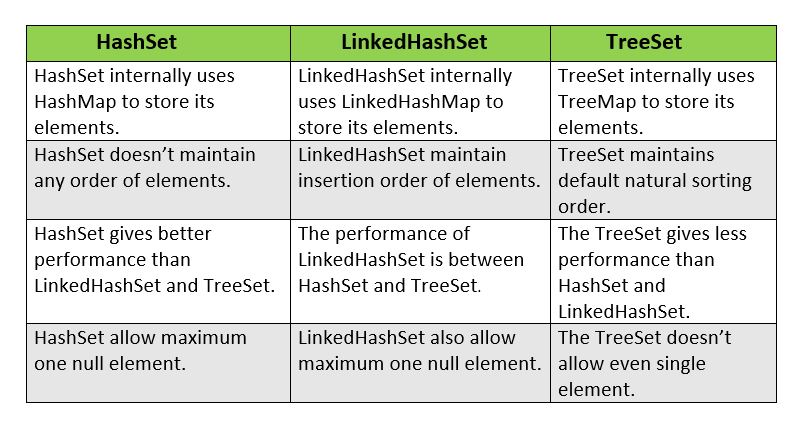
Question 86.
Difference between HashSet, LinkedHashSet, and TreeSet.
Answer:
The HashSet, LinkedHashSet, and TreeSet all three are the Set implementation but there are some differences between them which are shown below:
Question 87.
What is the difference between the Comparable and Comparator interface?
Answer:
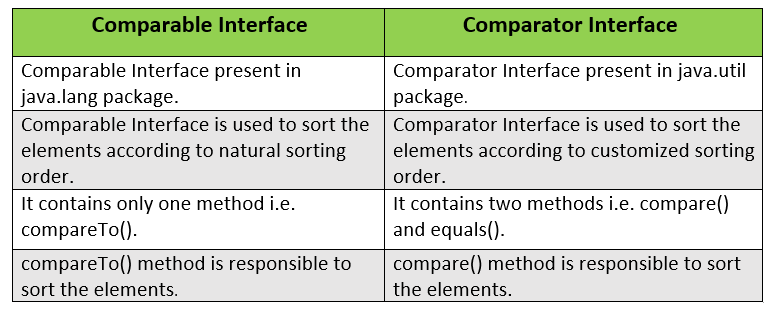
Question 88.
What is the difference between Set and Map?
Answer:
The differences between Set and Map are given below:
- Set contains only values whereas Map contains key values pair.
- Set doesn’t allow duplicates values whereas Map contains unique keys and duplicates values.
- Set only allowed one null element whereas Map allowed only a single null key and any number of null values.
Question 89.
What is the difference between HashSet and HashMap?
Answer:
The differences between HashSet and HashMap are given below:
- HashSet contains only values whereas HashMap contains key values pair.
- HashSet doesn’t allow duplicates values whereas HashMap contains unique key and duplicates values.
- HashSet implements Set interface whereas HashMap implements Map interface.
- HashSet only allowed one null element whereas HashMap allowed only a single null key and any number of null values.
Question 90.
What is the difference between HashMap, LinkedHashMap, and TreeMap?
Answer:
The main difference between HashMap, LinkedHashMap, and TreeMap is given below:
- HashMap: HashMap doesn’t maintain insertion order.
- LinkedHashMap: LinkedHashMap maintains the insertion order.
- TreeMap: TreeMap maintains the sorted order of keys.
Question 91.
What are the differences between HashMap and HashTable?
Answer:
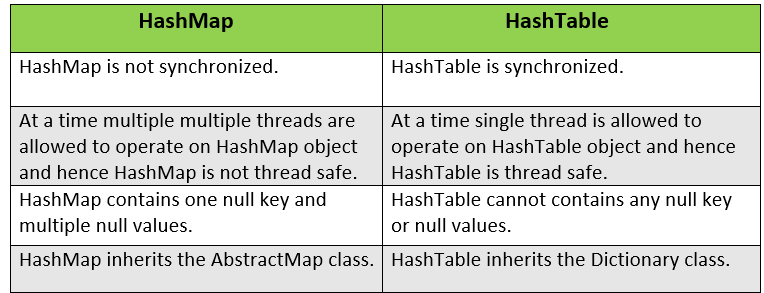
Question 92.
What is the difference between Collection and Collections?
Answer:
The Collection is an interface that can be used to represent a group of individual objects as a single entity whereas Collections is a utility class present in java.util package. The Collections defines several utility methods(like searching and sorting) for collection objects.
Question 93.
What is the difference between the hashCode() and equals() method?
Answer:
The hashCode() method is used to returns a hashcode value. It is an integer value. The equals() method is used to check the equality of two objects, two objects are equals if and only if they are present in the same memory address.
Java Serialization Interview Questions and Answers
Question 94.
What is Serialization?
Answer:
Serialization in Java is a technique of converting the state of an object into a byte stream. By usingFileOutputStream and ObjectOutputStream classes we can achieve Serialization in Java.
Question 95.
What is Deserialization?
Answer:
Deserialization in Java is a mechanism of rebuilding the object from a byte stream or we can say that it is a reverse process of serialization. By using FileInputStream and ObjectInputStream classes we can achieve Deserialization in Java.
Question 96.
What is the purpose of the transient keyword?
Answer:
Transient is a keyword in Java that is used in Serialization. It is applicable only for variables. At the time of serialization if you don’t want to serialize the value of a particular object for security concern then we should go for the transient keyword in Java. At the time of serialization when we declared a variable as transient JVM ignore the original value of a transient variable and set a default value to the file. Hence we can say that transient means not to serialize.
Question 97.
What is an object graph in Serialization?
Answer:
Whenever we are serializing an object the set of all object that contains the reference from that object will be serialized automatically. This group of a set is known as Object Graph. In Object Graph every object should be serializable. If at least one object is non-serializable then we will get a runtime exception saying NotSerializableException.
Question 98.
What is the need for customized serialization?
Answer:
In default Serialization, because of the transient keyword, there may be a chance of loss of information to recover this loss of information then we should go for Customized Serialization in Java.
Question 99.
What is Externalization?
Answer:
In Serialization total object is saved to the file and it is not possible to save part of an object which creates a performance problem. To overcome this problem we should go for Externalization in Java. An object is said to be externalizable if and only if a corresponding class implements the Externalizable interface. Externalizable is an interface that is present in java.io. package and it is the child interface of Serializable.
Question 100.
What is the advantage of Externalization?
Answer:
The main advantage of Externalization over Serialization is we can save either the total object or part of an object so that the relative performance will be improved.
Question 101.
What are the differences between Serialization and Externalization?
Answer:
The differences between Serialization and Externalization are given below:
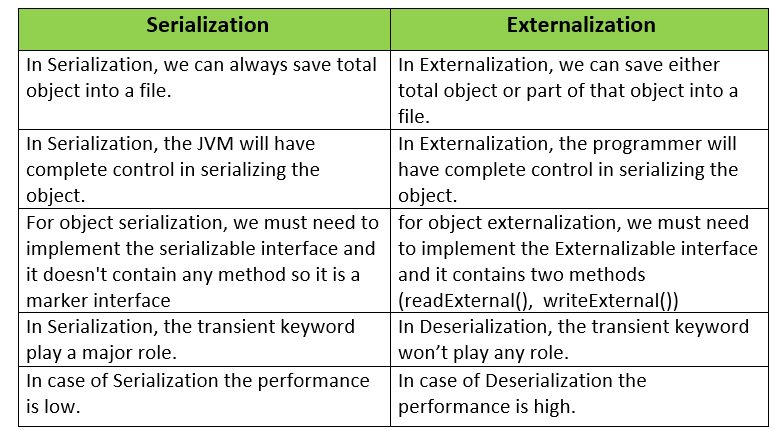
Question 102.
What is SerialVersionUID?
Answer:
During Serialization, the JVM creates a version number for each serializable class this version number is called SerialVersionUID. The SerialVersionUID is used to ensure that the same class(that was used during serialization) is loaded during deserialization.

