Files in Python:
Python file handling is a way of saving program output to a file or reading data from a file. File handling is a crucial concept in the programming world. File management is used in almost every form of project. Assume you are constructing an inventory management system. You have data in the inventory management system related to sales and purchases, thus you must save that data somewhere. Using Python’s file management, you can save that data to a file. You must be given data in the form of a comma-separated file or a Microsoft Excel file if you wish to conduct data analysis. Using file handling, you can read data from a file and write output back into it.
Given a file, the task is to read a given file and count the number of words whose length is greater than 5 in the given file in python
- Python Program to Count Words in a Text File those are Ending with Alphabet “e”
- Python Program to Count Number of Digits in a Text File
- Python Program to Reverse Each Word in a Text File
Program to Read a Text File and Count the Number of Words whose Length is Greater than 5 in Python
Below is the full approach for reading a given file and counting the number of words whose length is greater than 5 in the given file in python
Approach:
- Make a single variable to store the path of the file. This is a constant value. This value must be replaced with the file path from your own system in the example below.
- Open the file in read-only mode. In this case, we’re simply reading the contents of the file.
- Read the above file using the read() function(get the content) and store it in a variable.
- Take a variable(which gives the count of words with length>5 in a file) and initialize its value with zero.
- Split the above file text lines into list of words using the split() function and iterate in that list using the for loop.
- Get the length of each word is using the len() function and check if the length of each word is greater than 5 using the if conditional statement.
- If it is true, then increment the above count value by 1.
- Print the count of words with a length greater than 5 in a given file.
- The Exit of Program.
Below is the implementation:
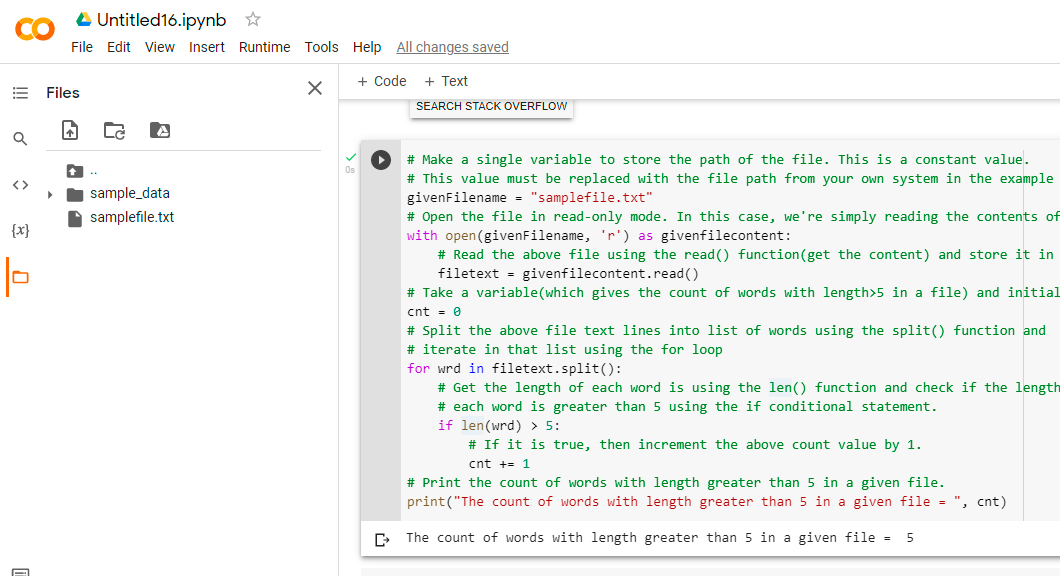
# Make a single variable to store the path of the file. This is a constant value.
# This value must be replaced with the file path from your own system in the example below.
givenFilename = "samplefile.txt"
# Open the file in read-only mode. In this case, we're simply reading the contents of the file.
with open(givenFilename, 'r') as givenfilecontent:
# Read the above file using the read() function(get the content) and store it in a variable
filetext = givenfilecontent.read()
# Take a variable(which gives the count of words with length>5 in a file) and initialize its value with zero.
cnt = 0
# Split the above file text lines into list of words using the split() function and
# iterate in that list using the for loop
for wrd in filetext.split():
# Get the length of each word is using the len() function and check if the length of
# each word is greater than 5 using the if conditional statement.
if len(wrd) > 5:
# If it is true, then increment the above count value by 1.
cnt += 1
# Print the count of words with length greater than 5 in a given file.
print("The count of words with length greater than 5 in a given file = ", cnt)
Output:
The count of words with length greater than 5 in a given file = 5
File Content:
hello this is btechgeeks sample file specific python codes Summary
Explanation:
- The file path is stored in the variable ‘file name.’ Change the value of this variable to the path of your own file.
- Dragging and dropping a file onto the terminal will show its path. The code will not run unless you change the value of this variable.
- The file will be opened in reading mode. Use the open() function to open a file. The path to the file is the method’s first parameter, and the mode to open the file is the method’s second parameter.
- When we open the file, we use the character ‘r’ to signify read-mode.
- Iterate in the given line using For loop and count all the characters using a temporary count variable
Google Colab Images:
Files and Code: