The Observer Design Pattern “define a one-to-many dependency between objects so that when one object changes state, all its dependents are notified and updated automatically” as per GOF.
There are two actors involved in observer pattern:
- Publisher(Subject) : The publisher provides an interface for adding and removing observers from the publisher list of observers. It also contains a method for notifying observers. It notifies all observer whenever it’s state changes.
- Observers : All observers implements an interface having a method to notify observer. Publisher published the update through this interface only. An observer will subscribe itself to publisher and will not monitor whether the state of publisher has changed or not.
- Publisher(subject) provides an Observer interface for the classes who wants to get notifies when state of the publisher changes.
- Publisher maintains a list of observers subscribed to it.
- Any number of observers can subscribe to Publisher.
- Observers can add or remove itself anytime.
- Either publisher can pass the new state information to observers while notifying them(push approach) or Observers can pull the data of their interest from publisher after getting notified by publisher.
Real world Example:- Magazine Subscription
Mark is a regular reader of a weekly tech magazine TechPhilia. He wants to read this magazine every week as soon as a new edition gets published. He subscribes to this magazine by visiting magazine publisher’s website. Now, whenever a new edition of TechPhilia release the magazine subscriber automatically send him the latest edition of magazine. If he wants he can unsubscribe himself from magazine publisher’s website to stop receiving magazines.
In above example, Magazine publisher is the subject and Mark is the Observer who is subscribed to Magazine publisher. Whenever a new magazine release(state of the subject changes), Mark gets the latest edition(Observer gets notified).
Advantages of Observer Pattern
- Publisher and Observers are loosely coupled. The only thing publisher knows about the observer is that it implements Observer interface.
- We can add or remove observers at runtime.
- Both Publisher and Observer can be modified independently without affecting each other’s implementation. Publisher and Observers should ensure that they are implementing their corresponding interfaces.
When we should use Observer Pattern
- When multiple object needs the latest state information an object whenever it changes.
- When we have to maintain consistency in the state of the multiple objects. When one changes others must also change.
- When we want to add or remove observers dynamically on runtime.
- When we want to decouple publisher and observers implementation.
Implementation of Observer Design Pattern
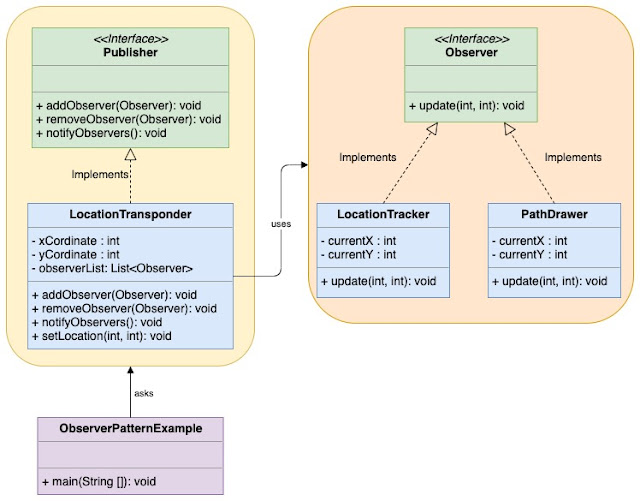
Every observer must implement ‘Observer’ interface, If they want to subscribe to publisher’s notifications.
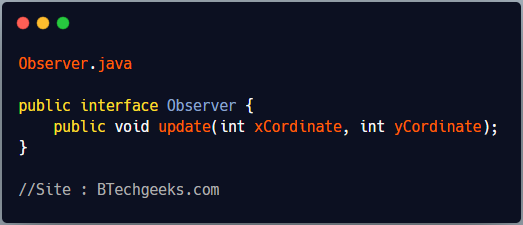
Observer.java
public interface Observer {
public void update(int xCordinate, int yCordinate);
}
Publisher provides an interface for adding and removing observers and a notification method.
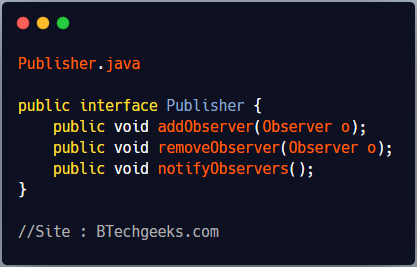
Publisher.java
public interface Publisher {
public void addObserver(Observer o);
public void removeObserver(Observer o);
public void notifyObservers();
}
LocationTransponder is the concrete implementation of Publisher. It maintains a list of observers subscribed to it. Whenever it’s location changes it notify all observers.
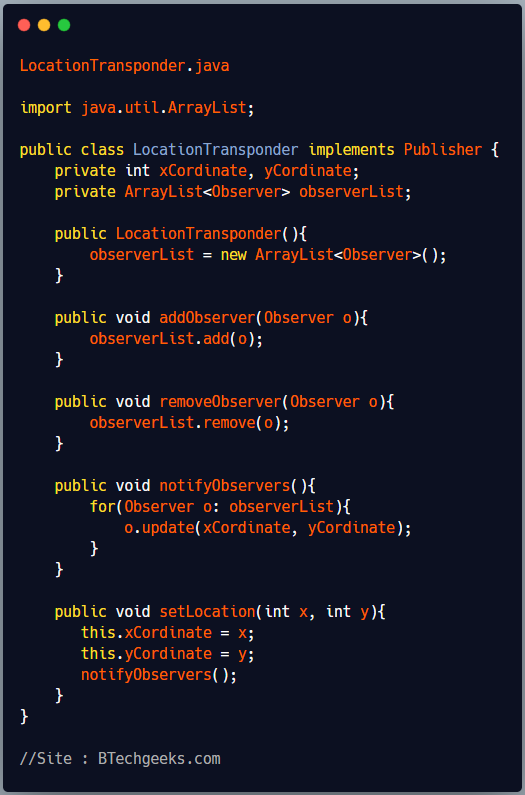
LocationTransponder.java
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class LocationTransponder implements Publisher {
private int xCordinate, yCordinate;
private ArrayList<Observer> observerList;
public LocationTransponder(){
observerList = new ArrayList<Observer>();
}
public void addObserver(Observer o){
observerList.add(o);
}
public void removeObserver(Observer o){
observerList.remove(o);
}
public void notifyObservers(){
for(Observer o: observerList){
o.update(xCordinate, yCordinate);
}
}
public void setLocation(int x, int y){
this.xCordinate = x;
this.yCordinate = y;
notifyObservers();
}
}
LocationTracker and PathDrawer are implementation of Observer interface. Objects of both classes can subscribe to LocationTransponder publisher.
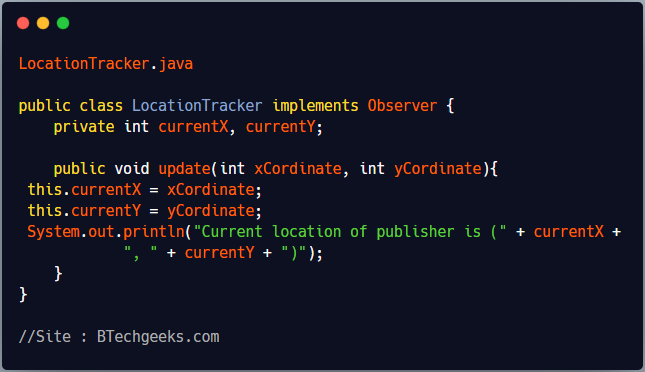
LocationTracker.java
public class LocationTracker implements Observer {
private int currentX, currentY;
public void update(int xCordinate, int yCordinate){
this.currentX = xCordinate;
this.currentY = yCordinate;
System.out.println("Current location of publisher is (" + currentX +
", " + currentY + ")");
}
}
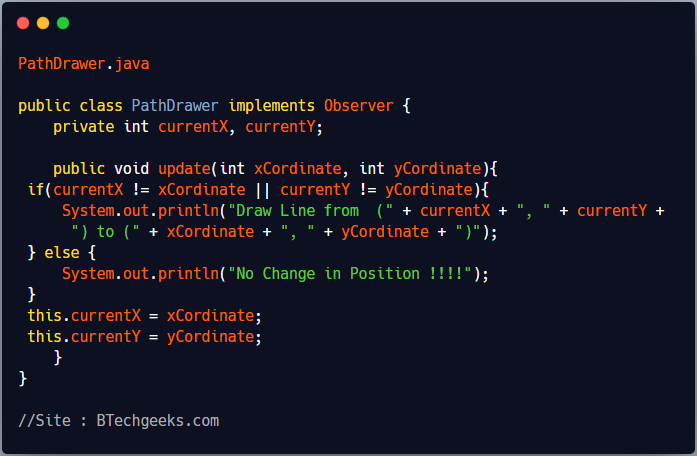
PathDrawer.java
public class PathDrawer implements Observer {
private int currentX, currentY;
public void update(int xCordinate, int yCordinate){
if(currentX != xCordinate || currentY != yCordinate){
System.out.println("Draw Line from (" + currentX + ", " + currentY +
") to (" + xCordinate + ", " + yCordinate + ")");
} else {
System.out.println("No Change in Position !!!!");
}
this.currentX = xCordinate;
this.currentY = yCordinate;
}
}
ObserverPatternExample is the client class which creates instance of LocationTransponder(publisher or subject) LocationTracker and PathDrawer(observers). It subscribe observers to LocationTransponder and changes the position of the LocationTransponder to notify observers.
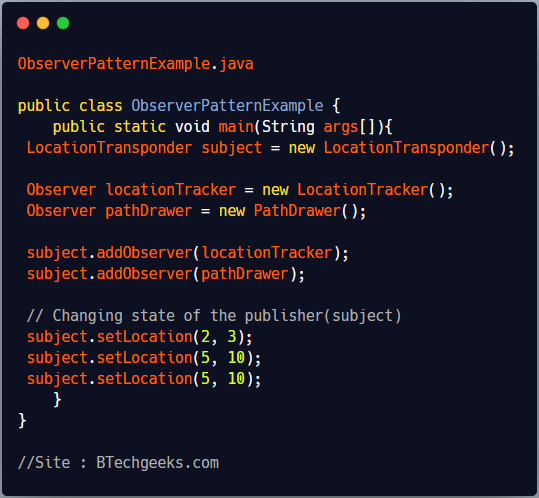
ObserverPatternExample.java
public class ObserverPatternExample {
public static void main(String args[]){
LocationTransponder subject = new LocationTransponder();
Observer locationTracker = new LocationTracker();
Observer pathDrawer = new PathDrawer();
subject.addObserver(locationTracker);
subject.addObserver(pathDrawer);
// Changing state of the publisher(subject)
subject.setLocation(2, 3);
subject.setLocation(5, 10);
subject.setLocation(5, 10);
}
}
Output
Current location of publisher is (2, 3) Draw Line from (0, 0) to (2, 3) Current location of publisher is (5, 10) Draw Line from (2, 3) to (5, 10) Current location of publisher is (5, 10) No Change in Position !!!!
