The Composite design pattern allows us to arrange objects into tree structures to represent part-whole hierarchies. It allows client to treat individual objects as well as collection of objects in similar manner. For client, the interface to interact with individual objects and composites remains the same, client doesn’t require different code for handling individual or collection of objects.
Composite pattern comes under structural design pattern as it provide one of the best ways to arrange similar objects in hierarchical order. A composite object may contains a collection object, where each object itself can be composite.
Advantages of Composite Pattern
- It provides a hierarchical tree structure to represent composite and individual objects.
- It allows clients treat individual objects and compositions of objects uniformly.
- We can change the structure of tree any time by calling methods of composite objects like addNode, removeNode etc.
When we should use Composite Pattern
- When multiple objects expose the same interface as each of them separately.
- When client needs a common interface to interact with individual objects and composite structure.
- When we need to represent the relationship between the objects as a tree.
Implementation of Composite Design Pattern
We will define a Teacher.java class, which will act as a Component of Composite pattern. It contains a list of teachers directly reporting to him.
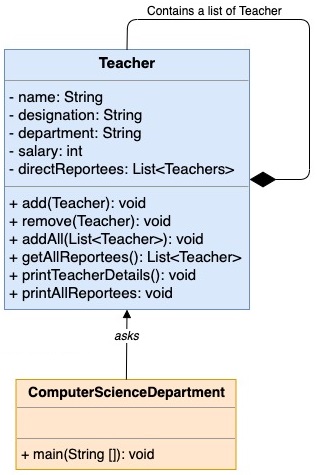
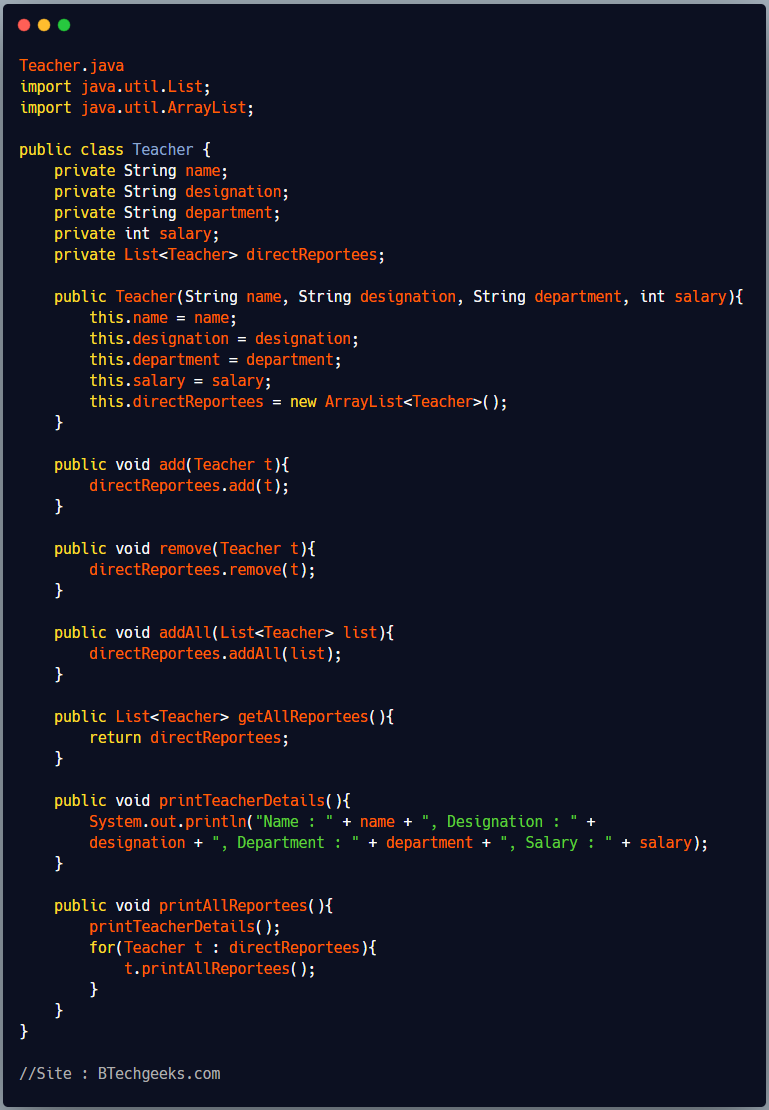
Teacher.java
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Teacher {
private String name;
private String designation;
private String department;
private int salary;
private List<Teacher> directReportees;
public Teacher(String name, String designation, String department, int salary){
this.name = name;
this.designation = designation;
this.department = department;
this.salary = salary;
this.directReportees = new ArrayList<Teacher>();
}
public void add(Teacher t){
directReportees.add(t);
}
public void remove(Teacher t){
directReportees.remove(t);
}
public void addAll(List<Teacher> list){
directReportees.addAll(list);
}
public List<Teacher> getAllReportees(){
return directReportees;
}
public void printTeacherDetails(){
System.out.println("Name : " + name + ", Designation : " +
designation + ", Department : " + department + ", Salary : " + salary);
}
public void printAllReportees(){
printTeacherDetails();
for(Teacher t : directReportees){
t.printAllReportees();
}
}
}
ComputerScienceDepartment.java creates a heirarchical tree structure of teachers of ComputerScienceDepartment of a college, where all AssistantProfessors report to Professor and all Professors report to HOD. It uses the same Teacher class interface to interact with individual teacher objects as well as whole teacher tree structure.
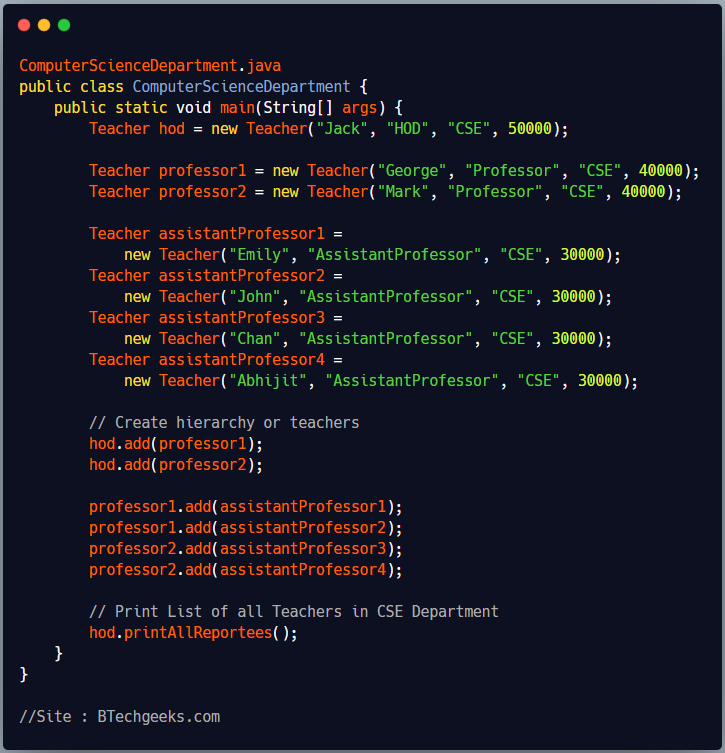
ComputerScienceDepartment.java
public class ComputerScienceDepartment {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Teacher hod = new Teacher("Jack", "HOD", "CSE", 50000);
Teacher professor1 = new Teacher("George", "Professor", "CSE", 40000);
Teacher professor2 = new Teacher("Mark", "Professor", "CSE", 40000);
Teacher assistantProfessor1 =
new Teacher("Emily", "AssistantProfessor", "CSE", 30000);
Teacher assistantProfessor2 =
new Teacher("John", "AssistantProfessor", "CSE", 30000);
Teacher assistantProfessor3 =
new Teacher("Chan", "AssistantProfessor", "CSE", 30000);
Teacher assistantProfessor4 =
new Teacher("Abhijit", "AssistantProfessor", "CSE", 30000);
// Create hierarchy or teachers
hod.add(professor1);
hod.add(professor2);
professor1.add(assistantProfessor1);
professor1.add(assistantProfessor2);
professor2.add(assistantProfessor3);
professor2.add(assistantProfessor4);
// Print List of all Teachers in CSE Department
hod.printAllReportees();
}
}
Output
Name : Jack, Designation : HOD, Department : CSE, Salary : 50000 Name : George, Designation : Professor, Department : CSE, Salary : 40000 Name : Emily, Designation : AssistantProfessor, Department : CSE, Salary : 30000 Name : John, Designation : AssistantProfessor, Department : CSE, Salary : 30000 Name : Mark, Designation : Professor, Department : CSE, Salary : 40000 Name : Chan, Designation : AssistantProfessor, Department : CSE, Salary : 30000 Name : Abhijit, Designation : AssistantProfessor, Department : CSE, Salary : 30000
