NumPy cosh() Function:
To calculate the hyperbolic cosine of a value, use the cosh() function of NumPy module. The hyperbolic cosine of x is calculated as follows:
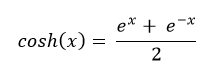
Here e= Euler’s number
Syntax:
numpy.cosh(x, out=None)
Parameters
x: This is required. It is an array (array-like) having elements for which the hyperbolic cosine(cosh) value is calculated.
out: This is optional. It is the location where the result will be saved. It must have a shape that the inputs broadcast to if it is provided. If None or not given, a newly allocated array is returned.
Return Value:
The hyperbolic cosine(cosh) value of each element of x is returned.
NumPy cosh() Function in Python
Example1
Approach:
- Import numpy module using the import keyword.
- Pass some random list as an argument to the array() function to create an array.
- Store it in a variable.
- Print the above-given array.
- Pass the above-given array as an argument to the cosh() function of the numpy module to get the hyperbolic cosine values of given array elements.
- Store it in another variable.
- Print the hyperbolic cosine values of given array elements.
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Import numpy module using the import keyword
import numpy as np
# Pass some random list as an argument to the array() function to
# create an array.
# Store it in a variable.
gvn_arry = np.array([20, 5, 8, 30, 12])
# Print the above given array.
print("The above given array is:")
print(gvn_arry)
# Pass the above given array as an argument to the cosh() function of the
# numpy module to get the hyperbolic cosine values of
# given array elements
# Store it in another variable.
hyprblic_cos_vals = np.cosh(gvn_arry)
# Print the hyperbolic cosine values of given array elements
print("The hyperbolic cosine values of given array elements:")
print(hyprblic_cos_vals)
Output:
The above given array is: [20 5 8 30 12] The hyperbolic cosine values of given array elements: [2.42582598e+08 7.42099485e+01 1.49047916e+03 5.34323729e+12 8.13773957e+04]
Example2
Approach:
- Import numpy module using the import keyword.
- Import math module using the import keyword.
- Give the array as static input and store it in a variable.
- Here we get pi values from math.pi of the math module.
- Pass the above-given array as an argument to the cosh() function of the numpy module to get the hyperbolic cosine values of given array elements.
- Store it in another variable.
- Print the hyperbolic cosine values of given array elements.
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Import numpy module using the import keyword
import numpy as np
# Import math module using the import keyword
import math
# Give the array as static input and store it in a variable
# Here we get pi values from math.pi of math module
gvn_arry = [math.pi / 4, 0, np.pi / 5, np.pi, math.pi / 2]
# Print the above given array.
print("The above given array is:")
print(gvn_arry)
# Pass the above given array as an argument to the cosh() function of the
# numpy module to get the hyperbolic cosine values of the
# given array elements
# Store it in another variable.
hyprblic_cos_vals = np.cosh(gvn_arry)
# Print the hyperbolic cosine values of given array elements
print("The hyperbolic cosine values of given array elements:")
print(hyprblic_cos_vals)
Output:
The above given array is: [0.7853981633974483, 0, 0.6283185307179586, 3.141592653589793, 1.5707963267948966] The hyperbolic cosine values of given array elements: [ 1.32460909 1. 1.20397209 11.59195328 2.50917848]