Let’s get into this tutorial and learn completely about What is the difference between final and immutable in Java? Apart from the final vs immutable with example explanation, you may also get to know what is final and immutable in java efficiently from here. Just click on the links available below and start understanding the concept thoroughly.
- What is Final in Java?
- What is Java Immutability?
- Difference between final and Immutable in Java
- Example Java program to demonstrate final vs immutability
What is Final in Java?
The Final in Java is a keyword that is relevant only to variables, methods, and classes. The Java Final Keyword is used to restrict the user to use variables, methods, and classes. The Final keyword is applicable for all the types of variables like instance variable, static variable, and local variable.
When a variable indicated as final and assigned a value, you can’t alter the value of the variable. The final method can’t be overridden by the child class. A class that is declared final cannot be extended.
What is Java Immutability?
Immutability means once we create an object it is not permissible to modify the content of that object. If any person trying to change the content if there is a change in the content with those changes a new object will be generated. If there are no changes in the content existing object will be reused.
Difference between Final and Immutable in Java
1. Final means that you can’t change the object reference to point to another reference or another object, but you can still mutate its state (by using the setter method). Where immutable means that the object’s actual value can’t be changed, but you can change its reference to another one.
2. The modifier final is applicable for variables not for objects, Whereas immutability applicable for objects not for variables.
3. Final ensures that the address of the object remains the same, Whereas the immutable suggest that we can’t change the state of the object once created.
4. By declaring the reference variable as final we are not going to get any immutability nature but we can perform any type of changes in the corresponding objects and we can’t reassign the reference variable to any new object.
Also Refer:
- How we can create our own immutable class in java?
- Difference between Statement Vs PreparedStatement Vs CallableStatement in java
Java program to demonstrate the difference between final and immutability:
class Test{
public static void main(String args[]){
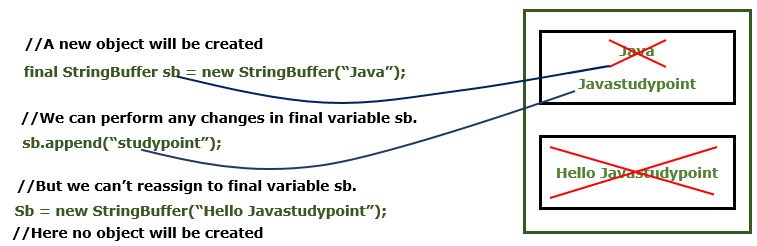
final StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("Java");
//Even though reference variable is final
//we can perform any changes to corresponding object.
sb.append("studypoint");
System.out.println(sb);
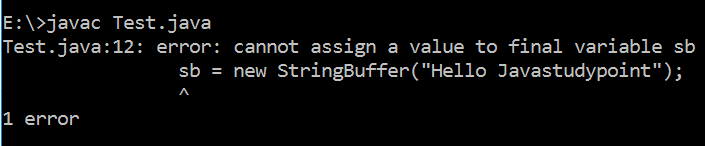
//Here, we will get compile time error because
//we can't reassign reference variable to any new object.
sb = new StringBuffer("Hello Javastudypoint");
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Output:
Diagrammatically representation of the above program
Explanation:
In the earlier diagram, we can see that we are creating an object of the StringBuffer class by making the reference variable final.
- By declaring a reference variable final, it does not mean that the object is immutable in nature.
- In the second line, we are performing append() operation on the created object and it is successfully changed.
- If the object is immutable, the above operation can’t be done.
- But it is executed successfully as we declare the reference variable as final, which means we can’t reassign anything to that reference variable again.
- Therefore when we try to create a new object of the StringBuffer class then it won’t be created and we will get a compile-time error.