NumPy arctanh() Function:
The arctanh() function of the NumPy module computes the inverse hyperbolic tangent values of the given array elements.
The inverse hyperbolic tangent of x is calculated as follows:
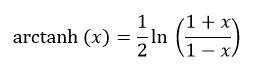
Syntax:
numpy.arctanh(array, out=None)
Parameters
array: This is required. The array items for which the inverse hyperbolic tangent values are to be computed. The value of each array element should be within a certain range (-1, 1).
out: This is optional.The output array’s shape. It is the location where the result will be stored. It must have a shape that the inputs broadcast to if it is provided. If None or not given, a newly allocated array is returned.
Return value
The inverse hyperbolic tangent values of each element of the given array is returned.
NumPy arctanh() Function in Python
Example#1: Using Built-in Functions (Static Input)
Approach:
- Import numpy module using the import keyword
- Give the array as static input using the array() function of the numpy module by passing some random list of numbers as an argument to it.
- Store it in a variable
- Calculate the inverse hyperbolic tangent values of each element of the given array using the arctanh() function of the numpy module and store it in another variable
- Print the inverse hyperbolic tangent values of the given array
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Import numpy module using the import keyword
import numpy as np
# Give the array as static input using the array() function of the numpy
# module by passing some random list of numbers as an argument to it.
# Store it in a variable
gvn_arry = np.array([0.3, 0.1, -0.7, 0.99])
# Calculate the inverse hyperbolic tangent values of each element of the given array
# using the arctanh() function of the numpy module and store it in another variable
rslt= np.arctanh(gvn_arry)
# Print the inverse hyperbolic tangent values of the given array
print("The inverse hyperbolic tangent values of the given array = ")
print(rslt)
Output:
The inverse hyperbolic tangent values of the given array = [ 0.3095196 0.10033535 -0.86730053 2.64665241]
Example#2: Using Built-in Functions (User Input)
Approach:
- Import numpy module using the import keyword.
- Give the list as user input using the list(),map(),split(),int functions and store it in a variable.
- Pass the above list as an argument to the array() function to get an array.
- Store it in another variable.
- Calculate the inverse hyperbolic tangent values of each element of the given array using the arctanh() function of the numpy module and store it in another variable
- Print the inverse hyperbolic tangent values of the given array
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Import numpy module using the import keyword
import numpy as np
# Give the list as user input using the list(),map(),split(),int functions
# and store it in a variable.
gvn_lst = list(map(float, input(
'Enter some random List Elements separated by spaces = ').split()))
# Pass the above list as an argument to the array() function to get an array.
# Store it in another variable
gvn_arry = np.array(gvn_lst)
# Calculate the inverse hyperbolic tangent values of each element of the given array
# using the arctanh() function of the numpy module and store it in another variable
rslt= np.arctanh(gvn_arry)
# Print the inverse hyperbolic tangent values of the given array
print("The inverse hyperbolic tangent values of the given array = ")
print(rslt)
Output:
Enter some random List Elements separated by spaces = 0.1 -0.2 0.88 -0.4 The inverse hyperbolic tangent values of the given array = [ 0.10033535 -0.20273255 1.37576766 -0.42364893]