Files In Python:
Python file readable: A file is a piece of data or information stored on a computer’s hard drive. You’re already familiar with a variety of file kinds, including music, video, and text files. Manipulation of these files is trivial with Python. Text files and binary files are the two types of files that are commonly used. Binary files contain binary data that can only be read by a computer, whereas text files include plain text.
For programmers and automation testers, Python file handling (also known as File I/O) is a crucial topic. Working with files is required in order to write to or read data from them.
In addition, if you didn’t know, I/O activities are the most expensive techniques via which software might fail. As a result, when implementing file processing for reporting or any other reason, you should proceed with caution. The construction of a high-performance application or a robust solution for automated software testing can benefit from optimizing a single file activity.
File readable() Method in Python:
The readable() method is a built-in function that produces a result True if the file is readable, False otherwise.
Syntax:
file.readable()
Parameters: This method doesn’t accept any arguments.
Return Value:
This method’s return type is <class ‘bool’>; it returns True if the file stream is readable and False if the file stream is not readable.
- Python Program to Count Number of Digits in a Text File
- Python open() Function with Examples
- Python Interview Questions on File Manipulation
File readable() Method with Examples in Python
Example
Approach:
- Make a single variable to store the path of the file. This is a constant value. This value must be replaced with the file path from your own system in the example below.
- Open the file in write mode. In this case, we’re writing the contents into the file.
- Apply readable() function to the given file to check if the file is readable or not and print the result.
- Close the given file using the close() function.
- Open the file in read-only mode. In this case, we’re simply reading the contents of the file.
- Apply readable() function to the given file to check if the file is readable or not and print the result.
- Close the given file using the close() function.
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
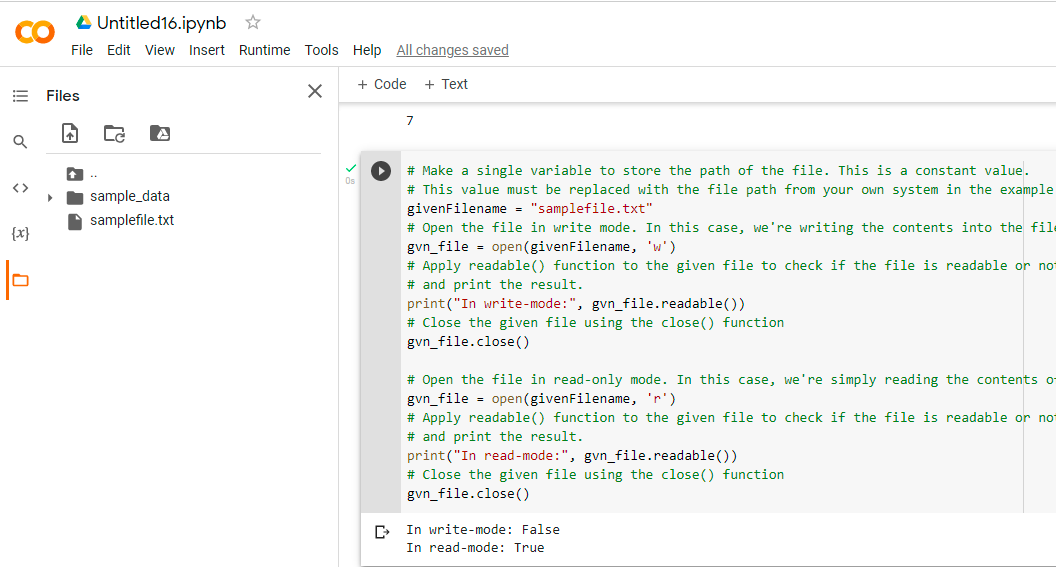
# Make a single variable to store the path of the file. This is a constant value.
# This value must be replaced with the file path from your own system in the example below.
givenFilename = "samplefile.txt"
# Open the file in write mode. In this case, we're writing the contents into the file.
gvn_file = open(givenFilename, 'w')
# Apply readable() function to the given file to check if the file is readable or not
# and print the result.
print("In write-mode:", gvn_file.readable())
# Close the given file using the close() function
gvn_file.close()
# Open the file in read-only mode. In this case, we're simply reading the contents of the file.
gvn_file = open(givenFilename, 'r')
# Apply readable() function to the given file to check if the file is readable or not
# and print the result.
print("In read-mode:", gvn_file.readable())
# Close the given file using the close() function
gvn_file.close()
Output:
In write-mode: False In read-mode: True
File Content:
Hello this is btechgeeks Good morning btechgeeks welcome to python-coding platform
Google Colab Images:
Files and Code: