Files in Python:
Python file handling is a way of saving program output to a file or reading data from a file. File handling is a crucial concept in the programming world. File management is used in almost every form of project. Assume you are constructing an inventory management system. You have data in the inventory management system related to sales and purchases, thus you must save that data somewhere. Using Python’s file management, you can save that data to a file. You must be given data in the form of a comma-separated file or a Microsoft Excel file if you wish to conduct data analysis. Using file handling, you can read data from a file and write output back into it.
File encoding Property in Python:
In Python, the encoding Property is a built-in property of the File object (IO object), and it is used to retrieve the file’s encoding format from the file object. “utf-8,” which stands for “Unicode Transformation Standard 8 bits,” is the default encoding format.
Syntax:
fileobject.encoding
Parameters: This property has no arguments
Return Value: This method’s return type is <class’str’>, and it returns the file’s encoding format.
- Python open() Function with Examples
- Python Program to Delete Specific Line from a Text File
- Python Program to Count Words in a Text File those are Ending with Alphabet “e”
File encoding Property with Examples in Python
Approach:
- Make a single variable to store the path of the file. This is a constant value. This value must be replaced with the file path from your own system in the example below.
- Open the file in write mode. In this case, we’re writing the contents into the file.
- Apply encoding function to the given file and print it.
- Close the given file using the close function.
- Open the file in append mode. In this case, we’re appending the contents into the file.
- Apply encoding function to the given file and print it.
- Close the given file using the close function.
- Open the file in write mode and pass encoding =’utf-16′ as the arguments to the open() function.
- Apply encoding function to the given file and print it.
- Close the given file using the close function.
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
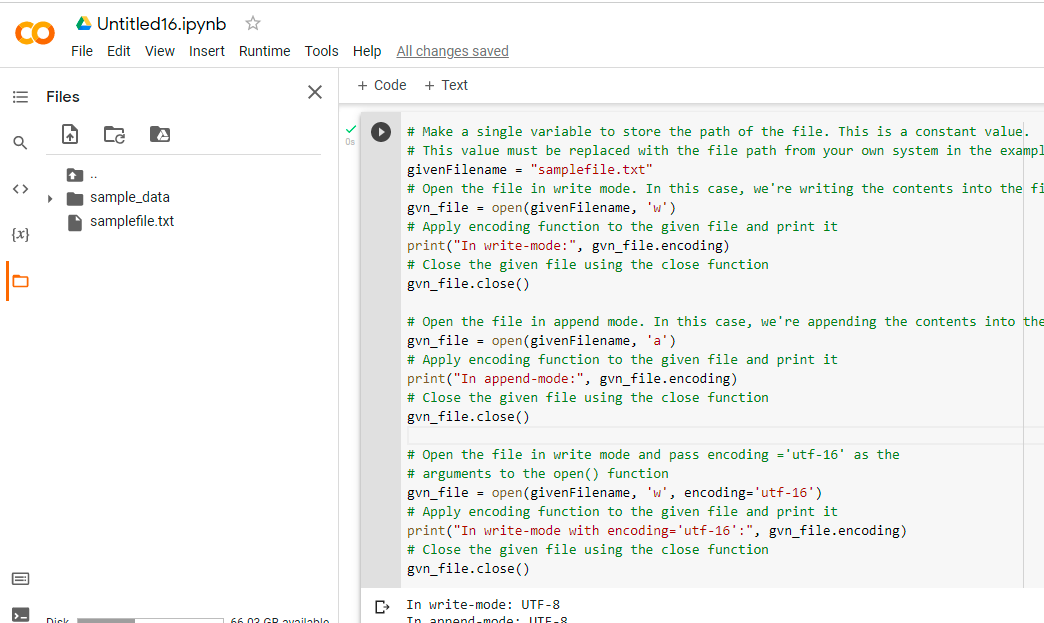
# Make a single variable to store the path of the file. This is a constant value.
# This value must be replaced with the file path from your own system in the example below.
givenFilename = "samplefile.txt"
# Open the file in write mode. In this case, we're writing the contents into the file.
gvn_file = open(givenFilename, 'w')
# Apply encoding function to the given file and print it
print("In write-mode:", gvn_file.encoding)
# Close the given file using the close function
gvn_file.close()
# Open the file in append mode. In this case, we're appending the contents into the file.
gvn_file = open(givenFilename, 'a')
# Apply encoding function to the given file and print it
print("In append-mode:", gvn_file.encoding)
# Close the given file using the close function
gvn_file.close()
# Open the file in write mode and pass encoding ='utf-16' as the
# arguments to the open() function
gvn_file = open(givenFilename, 'w', encoding='utf-16')
# Apply encoding function to the given file and print it
print("In write-mode with encoding='utf-16':", gvn_file.encoding)
# Close the given file using the close function
gvn_file.close()
Output:
In write-mode: UTF-8 In append-mode: UTF-8 In write-mode with encoding='utf-16': utf-16
File Content:
Hello this is btechgeeks Good morning btechgeeks welcome to python-coding platform
Google Colab Images:
Files and Code: