Files in Python:
One of the most important subjects for programmers and automation testers is Python file handling (also known as File I/O). It is necessary to work with files in order to write to or read data from them.
Also, if you didn’t know, I/O operations are the most expensive processes where a programme can go wrong. As a result, you must use extreme caution while implementing file processing for reporting or any other reason. Optimizing a single file action can help in the creation of a high-performing application or a reliable automated software testing solution.
Consider the following scenario: you’re planning to construct a large Python project with a large number of workflows. Then it’s unavoidable that you don’t make a log file. You’ll also be handling the log file’s read and write activities. Debugging huge applications with log files is a terrific way to go. It’s usually better to consider a scalable design from the start, as you won’t be sorry later if you didn’t.
File close() Method in Python:
Close() python: The close() function is a built-in Python method that is used to flush and close the IO object (file). It has no effect if we close a closed file.
Syntax:
fileobject.close()
Parameters: This method has no arguments
Return Value: This method doesn’t return anything. This method’s return type is <class ‘NoneType’>, which means it returns nothing.
- Python Program to Count Number of Digits in a Text File
- How to run Python scripts
- Python Interview Questions on File Manipulation
File close() Method with Examples in Python
Approach:
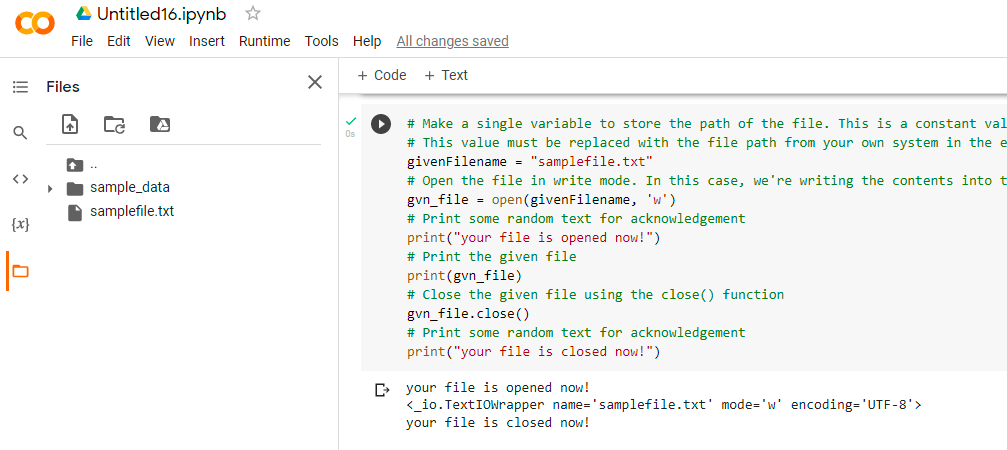
- Make a single variable to store the path of the file. This is a constant value. This value must be replaced with the file path from your own system in the example below.
- Open the file in write mode. In this case, we’re writing the contents into the file.
-
Print some random text for acknowledgment.
-
Print the given file.
- Close the given file using the close() function.
-
Print some random text for acknowledgment.
- The Exit of the Program.
Below is the implementation:
# Make a single variable to store the path of the file. This is a constant value.
# This value must be replaced with the file path from your own system in the example below.
givenFilename = "samplefile.txt"
# Open the file in write mode. In this case, we're writing the contents into the file.
gvn_file = open(givenFilename, 'w')
# Print some random text for acknowledgment
print("your file is opened now!")
# Print the given file
print(gvn_file)
# Close the given file using the close() function
gvn_file.close()
# Print some random text for acknowledgment
print("your file is closed now!")
Output:
your file is opened now! <_io.TextIOWrapper name='samplefile.txt' mode='w' encoding='UTF-8'> your file is closed now!
File Content:
Hello this is btechgeeks Good morning btechgeeks welcome to python-coding platform
Google Colab Images:
Files and Code: