Python NumPy is the ultimate package in a python programming language that includes multidimensional array objects and a set of operations or routines to execute various operations on the array and process of the array. Where this numpy package is comprised of a function known as numpy.reshape() that performs converting a 1D array into a 2-D array of required dimensions (n x m). This function gives a new required shape without changing the data of the 1-D array.
This tutorial of Convert a 1D array to a 2D Numpy array or Matrix in Python helps programmers to learn the concept precisely and implement the logic in required situations. However, you can also learn how to construct the 2D array row-wise and column-wise, from a 1D array from this tutorial.
- How to convert a 1D array to a 2D Numpy array or Matrix in Python
- Reshape 1D array to 2D array
- Reshaped 2D array in view of a 1D array
- Convert a 1D numpy array to a 3D numpy array using numpy.reshape()
- Convert 1D numpy array to a 2D numpy array along the column
- Convert 2D array to 1D array as Copy
How to convert a 1D array to a 2D Numpy array or Matrix in Python
Converting 1d array to 2d array: In this section, python learners will find the correct explanation on how to convert a 1D Numpy array to a 2D Numpy array or matric with the help of reshape() function.
One dimensional array contains elements only in one dimension.
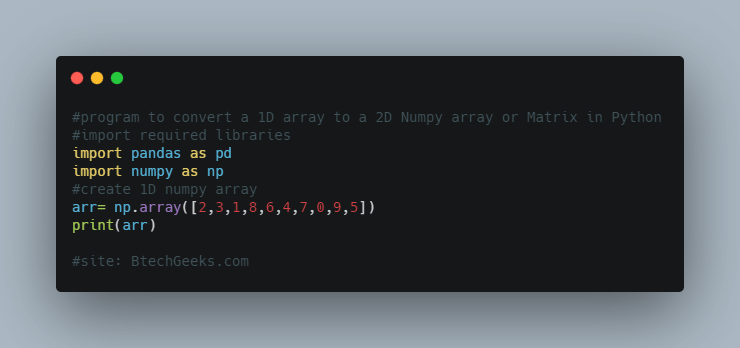
Let’s try with an example:
#program #import required libraries import pandas as pd import numpy as np #create 1D numpy array arr= np.array([2,3,1,8,6,4,7,0,9,5]) print(arr)
Output : [2 3 1 8 6 4 7 0 9 5]
- Python Programming – NumPy
- Python: numpy.ravel() function Tutorial with examples
- Sorting 2D Numpy Array by column or row in Python | How to sort the NumPy array by column or row in Python?
Now we will convert it into a 2D array of shape 5X2 i.e 5 rows and 2 columns like shown below:
[[0 1 2 3 4] [5 6 7 8 9]]
Reshape 1D array to 2D array
First, import the numpy module,
import numpy as np
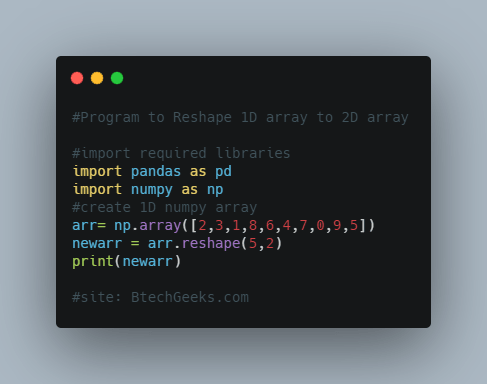
Now to change the shape of the numpy array, we will use the reshape() function of the numpy module,
#Program:Reshape 1D array to 2D array #import required libraries import pandas as pd import numpy as np #create 1D numpy array arr= np.array([2,3,1,8,6,4,7,0,9,5]) newarr = arr.reshape(5,2) print(newarr)
Output:
[[2 3] [1 8] [6 4] [7 0] [9 5]]
First, we import the numpy module and then passed the 1D array as the first argument and the new shape i.e a tuple (5,2) as the second argument. It returned the 2D array.
Note: The new shape of the array must be compatible with the original shape of the input array, if not then it will raise ValueError.
numpy.reshape() function
- It is used to give a new shape to an array without changing its data.
- It returns the new view object(if possible, otherwise returns a copy) of the new shape.
Reshaped 2D array in view of a 1D array
If possible the function returns a view of the original and any modification in the view object will also affect the original input array.
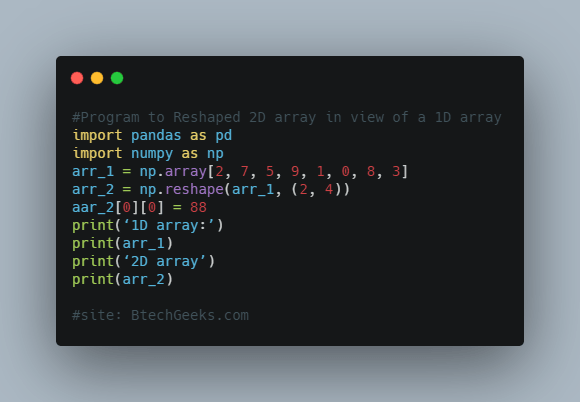
Example:
#Program:Reshaped 2D array in view of a 1D array import pandas as pd import numpy as np arr_1 = np.array[2, 7, 5, 9, 1, 0, 8, 3] arr_2 = np.reshape(arr_1, (2, 4)) aar_2[0][0] = 88 print(‘1D array:’) print(arr_1) print(‘2D array’) print(arr_2)
Output:
1D array: [88 7 5 9 1 0 8 3] 2D array: [[88 7 5 9] [ 1 0 8 3]]
Convert a 1D numpy array to a 3D numpy array using numpy.reshape()
In case, we have 12 elements in a 1D numpy array,
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12])
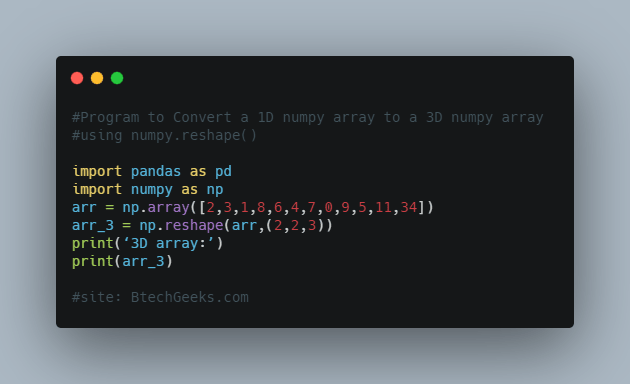
Now, let’s convert this 1D numpy array to a 3D numpy array:
#Program:Convert a 1D numpy array to a 3D numpy array using numpy.reshape() import pandas as pd import numpy as np arr = np.array([2,3,1,8,6,4,7,0,9,5,11,34]) arr_3 = np.reshape(arr,(2,2,3)) print(‘3D array:’) print(arr_3)
Output:
3D array: [[[2 3 1] [8 6 4]] [[7 0 9] [5 11 34]]]
Here, the first argument is a 1D array and the second argument is the tuple (2, 2, 3).
It returned a 3D view of the passed array.
Convert 1D numpy array to a 2D numpy array along the column
After converting a 1D array to a 2D array or matrix in the above example, the items from the input array will be shown row-wise i.e.
- 1st row of a 2D array was created from items at index 0 to 2 in the input array
- 2nd row of a 2D array was created from items at index 3 to 5 in the input array
- 3rd row of a 2D array was created from items at index 6 to 8 in the input array
Now suppose we want to convert a 2D array column-wise so we have to pass the order parameter as ‘F’ in the reshape() function.
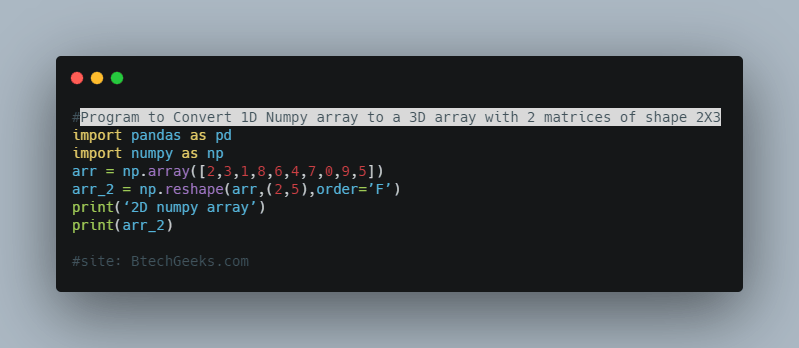
#Program:Convert 1D Numpy array to a 3D array with 2 matrices of shape 2X3 import pandas as pd import numpy as np arr = np.array([2,3,1,8,6,4,7,0,9,5]) arr_2 = np.reshape(arr,(2,5),order=’F’) print(‘2D numpy array’) print(arr_2)
Output: 2D numpy array: [[0 2 4 6 8] [1 3 5 7 9]]
Convert 2D array to 1D array as Copy
Suppose we want to create a 2D copy of the 1D numpy array then use the copy() function along with reshape() function.
Let’s try with an example:
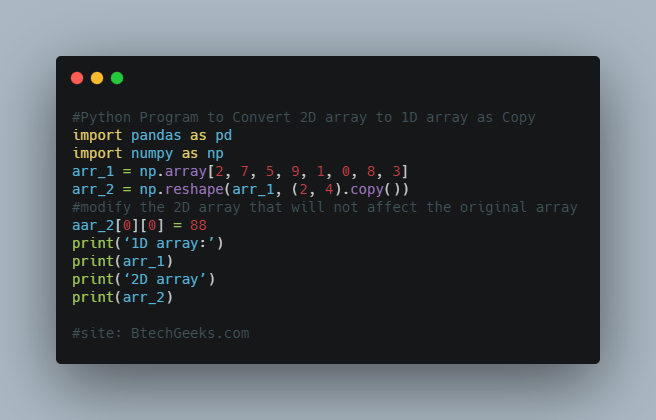
#Program:Convert 2D array to 1D array as Copy import pandas as pd import numpy as np arr_1 = np.array[2, 7, 5, 9, 1, 0, 8, 3] arr_2 = np.reshape(arr_1, (2, 4).copy()) #modify the 2D array that will not affect the original array aar_2[0][0] = 88 print(‘1D array:’) print(arr_1) print(‘2D array’) print(arr_2)
Output:
1D array: [2 7 5 9 1 0 8 3] 2D array: [[88 7 5 9] [ 1 0 8 3]]
Here, the 2D array is created of the 1D array. If you want to change the 2D array without changing the original array, just use the copy() function and the reshape() function.

