Searching for well-organized and detailed explanation tutorials on Java Operators or other Java concepts? BTech Geeks is the perfect one-stop destination for you all beginners & also experienced programmers. Today, in this java tutorial, we are providing complete information about Logical Operators in Java with Examples. Also, you will learn the types of java logical operators with the help of prevailing tables & examples.
This Java Logical Operators Tutorial Contains:
- Java Operators
- Java Logical Operators
- && (Logical AND) Operator
- || (Logical OR) Operator
- ! (Logical Not Operator)
- Example of Logical Operators in Java
Java Operators
Operators are special symbols that perform specific operations on one, two, or three operands, and then return a result. There are different types of operators are available in java which are given below:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Unary Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- BitWise Operators
- Ternary Operators
- InstanceOf Operators
Java Logical Operators
Logical Operators in Java works on boolean operands. It is also known as Boolean Logical Operators. It operates on two boolean values, which return boolean values(true/false) as a result. There are basically three types of logical operators used in Java.
| Operator | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
&& (Logical AND) |
expression1 && expression2 | true only if both expression1 and expression2 are true |
|| (Logical OR) |
expression1 || expression2 | true if either expression1 or expression2 is true |
! (Logical NOT) |
!expression | true if expression is false and vice versa |
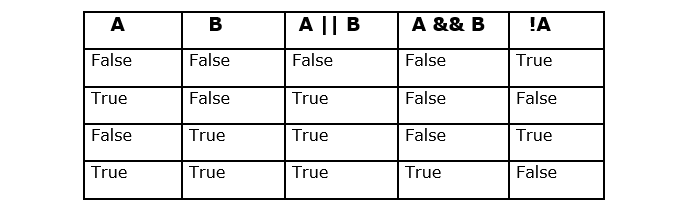
The below image represents what are the possible values of A && B, A || B, and !A, if you assume two operands A and B:
Do Refer:
&& (Logical AND) Operator
This operator returns true if both conditions are true. If we have taken two conditions A and B then the possible values of A && B are shown in the below table:
| A | B | A && B |
| True | True | True |
| False | True | False |
| True | False | False |
| False | False | False |
|| (Logical OR) Operator
The logical || operator allows two operands. This operator returns true if at least one condition is true. Assume we have two conditions A and B. Now, check the possible values of A || B in the below-resulting table.
| A | B | A || B |
| True | True | True |
| False | True | True |
| True | False | True |
| False | False | False |
! (Logical Not Operator)
This operator reverses the value of the operand. If the value is true, then it returns false, and if it is false, then it returns true. An exclamation sign (!) is the representation of this logical operator. It accepts a single operand ie., A. Then it returns the opposite possible Value of A.
| A | !A |
| True | False |
| False | True |
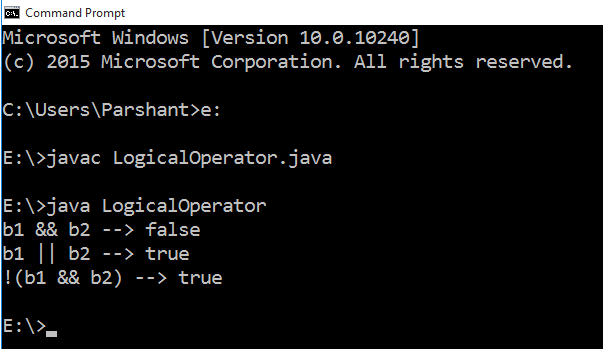
Example of Logical Operators in Java
class LogicalOperator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Variables Definition and Initialization
boolean b1 = true, b2 = false;
//Logical AND Operation
System.out.println("b1 && b2 --> " + (b1 && b2));
//Logical OR Operation
System.out.println("b1 || b2 --> " + (b1 || b2) );
//Logical Not Operation
System.out.println("!(b1 && b2) --> " + !(b1 && b2));
}
}
Output: