Nested if else statements java: In this tutorial, you will learn what is a nested-if statement and its syntax, flowchart, and example. Basically, we can control the flow of execution of a program based on some conditions in java programming. Java control statements are divided into three categories such as selection, iteration, and jump. Make use of the direct links provided here & understand the concept of nested-if statement efficiently.
- Java nested-if Statement
- Nested-if Statment Syntax
- Flowchart of Nested If Statment in Java
- Variations of nested if
- Nested If in Java Programming Example
Java nested-if Statement
Nested if statement java: Java nested-if statement expresses an if statement inside another if statement. A nested-if is an if statement that is the target of another if or else statement. In nested-if, the inner if block condition executes only when outer if block condition is true.
Nested-if Statment Syntax
if(condition1){
//code to be executed for condition1
}
if(condition2){
//code to be executed for condition2
}
Flowchart of Nested If Statment in Java
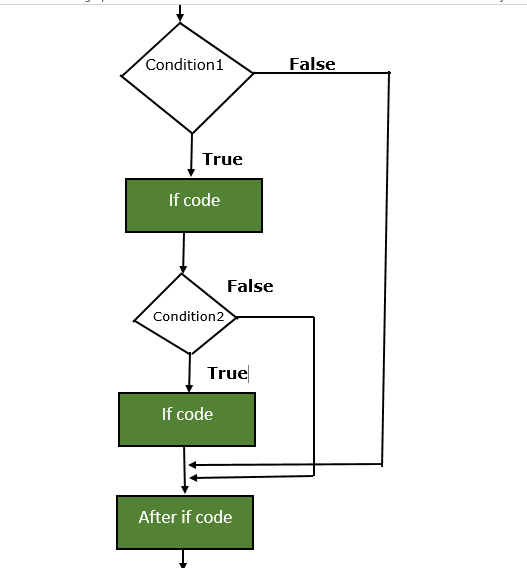
The execution flow of the Java Nested If statement is as follows:
- If Condition 1 is FALSE, then the Final statement will execute.
- If Test Condition 1 is TRUE, it will check for Test Condition 2
- If Condition 2 is TRUE, then the final statement will execute
- Else final statement executed.
Do Check:
Variations of nested if
Nested if else in java: We may also have an inner if statement that is contained in the if body of an outer if but isn’t the if body. Let’s see an illustration:
if ( num > 0 ) // Outer if
{
System.out.println( "Got here" ) ;
if ( num < 10 ) // Inner if
System.out.println( "num is between 0 and 10" ) ;
}
In this example, the body of outer if includes two statements, one of which is the inner if body.
This can’t be rewritten using && because the first println()statement only based on the outer condition.
Nested If in Java Programming Example:
class NestedIfExample{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 10, num2 = 5, num3 = 20, largestNumber;
if (num1 >= num2) {
if (num1 >= num3) {
largestNumber = num1;
} else {
largestNumber = num3;
}
} else {
if (num2 >= num3) {
largestNumber = num2;
} else {
largestNumber = num3;
}
}
System.out.println("Largest number is: " + largestNumber);
}
}
Output:
The largest number is: 20

