Which driver is called as thin-driver in jdbc: JDBC Driver is a software component that is used to interact with the java application with the database. The purpose of JDBC driver is to convert java calls into database-specific calls and database-specific calls into java calls.
Types of JDBC Drivers:
- JDBC-ODBC bridge driver.
- Native API driver
- Network protocol driver.
- Pure java driver.
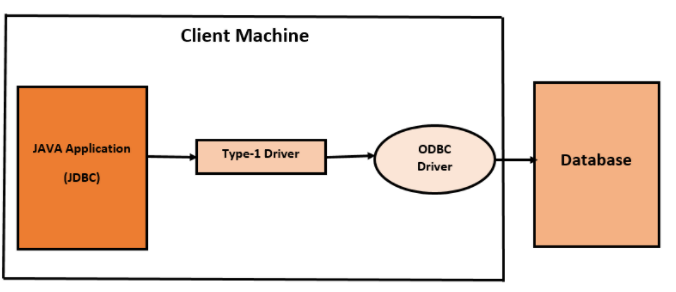
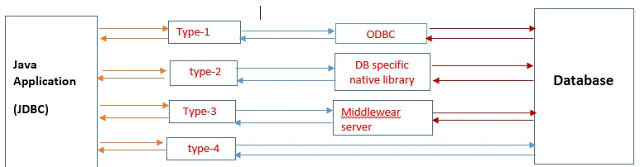
1) JDBC-ODBC bridge Driver :
- This driver is also known as Type-1 Driver. Internally this Driver will take the support of ODBC Driver to communicate with the database.Type-1 Driver convert JDBC calls into ODBC calls and ODBC Driver convert ODBC calls into database-specific calls.
- Using Type-1 Driver for prototyping only and not for production purposes.
- This driver can be provided by Sun Microsystem as a part of JDK.
Advantages :
- Type-1 Driver is database-independent driver.
- it is very easy to use.
- Not require to install this driver separately(By default in windows)
Disadvantages :
- It is the slowest driver.
- Type-1 driver internally depends upon ODBC driver so ODBC driver concept application only on window machine i.e. platform-dependent driver.
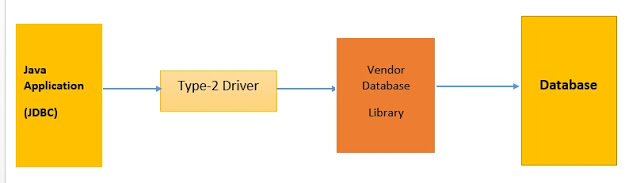
2) Native API Driver :
- Native API driver converts JDBC calls into database-specific native libraries calls and these calls are directly understood by the database engine.
- Large database vendors, such as Oracle and IBM, use the Type-2 driver for their enterprise databases.
- Type-2 Drivers aren’t architecturally compatible.
- Type-2 Drivers force developers to write platform-specific code.
Advantages :
- Good performance as compared to the type-1 driver.
- No ODBC Driver require.
- Type-2 Drivers are operating system-specific and compiled.
Disadvantages :
- It is a database-dependent driver.
- It is a platform-dependent driver.
- Only Oracle provides type-2 Driver
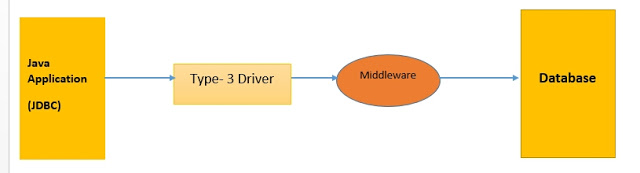
3) Network protocol driver:
- For database middle-ware, Type-3 JDBC drivers are pure Java drivers.
- java application communicates with Network Protocol driver. Network protocol driver converts JDBC calls into middle-wear specific calls, the middle-wear server communicates with database, middle-wear server convert middle-wear specific calls into database-specific calls.
Advantages :
- This driver does not directly communicate with the database. So it is database-independent driver. For any database, this driver is the same.
- It is fully written in Java. So it is platform-independent driver.
No client-side libraries are required.
Disadvantages:
- Network support is required on the client machine.
- When we change the database, we need to change the middle-wear code.
- Maintenance of Network Protocol driver becomes costly.
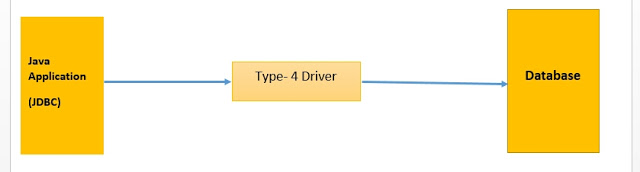
4) Pure Java Driver:
- It is also known as the Thin driver. The thin driver converts JDBC calls into database-specific calls directly.
- Thin driver directly communicates with the database by using database-specific native protocol provided by the database vendor.
- It is a platform, independent Driver.
Advantage:
- Better performance than all other drivers.
- Platform independent Driver.
- No software is required at the client-side or server side.
Disadvantages:
- Database dependent driver, because it is directly communicating with the database direct.
Which JDBC Drivers should be used :
Which driver is called as thin driver in jdbc: In our application, if you are using only one type of database may be an oracle,
MySQL then we should go for the type-1 driver.
Example: Standalone application,Small scale web application.
In our application, if you are using multiple databases highly recommended, you should go for the type-3 driver. Because the type-3 driver is database independent driver.
Example: large scale web application,Enterprise application.
To connect to multiple databases, developers can use type-2 Driver.
if no driver is available then we should go for type-4 driver
Differentiate between Thick and Thin Driver:
Thick Driver:
if the database driver requires some extra component to communicate with database such type of driver is called the Thick driver.
Example: Type-1,Type-2,Type-3 Driver.
Thin Driver:
if the database driver does not require some extra component to communicate with database such type of driver is called the Thin driver.
Example: Type-4 Driver.
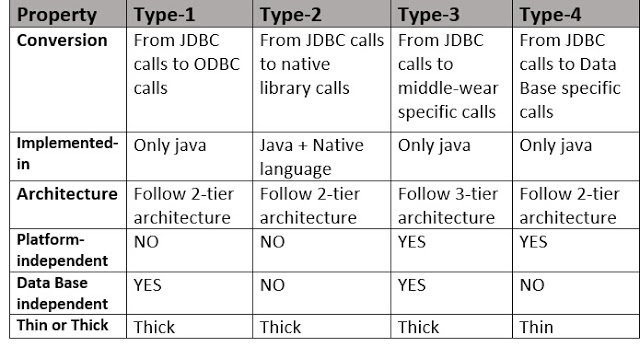
Comparison of all types of JDBC Drivers: