Java continue outer loop: A programming language uses control statements to control the flow of execution of a program. In Java programming, we can control the flow of execution of a program based on some conditions. Java control statements can be put into the following three categories: selection, iteration, and jump. In this tutorial, we will learn about the Java continue statement with example programs and workings. The jump statement can be used to transfer the control to other parts of the program. The java continues statement is one of the jump statements.
- Java Continue Statement
- Syntax of Java Continue
- Flow Diagram of Continue Statement
- Working of Java continue statement
- Continue Statement Example
- Java Continue Statement with Nested Loop
- Example of Continue with Nested Loop
- Java Continue Statement with Labeled for Loop
- Example of Labeled Continue Statement
- Java Continue Statement with Inner Loop
- Example on Continue with Inner Loop
- Java Continue Statement in while loop
- Example on Java Continue statement inside While loop
- Java Continue Statement in do-while loop
- Continue Statement in Java Example in Do-While loop
Java Continue Statement
The Java Continue Statement skips the current iteration of a for loop, while loop, and do-while loop. We can use a continue statement with all types of loops such as: for loop, while loop, and do-while loop. In the while and do-while loops, a continue statement causes control to be transferred directly to the conditional expression that controls the loop. In for loop, the control goes first to the iteration portion of the for statement and then to the conditional expression.
Syntax of Java Continue
continue;
Do Check:
Flow Diagram of Continue Statement
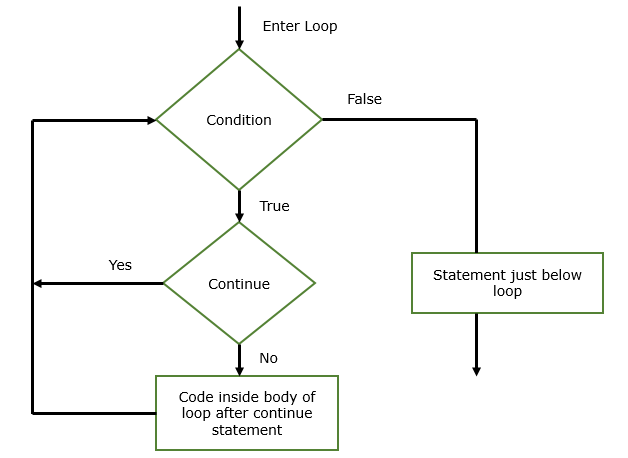
Working of Java continue statement
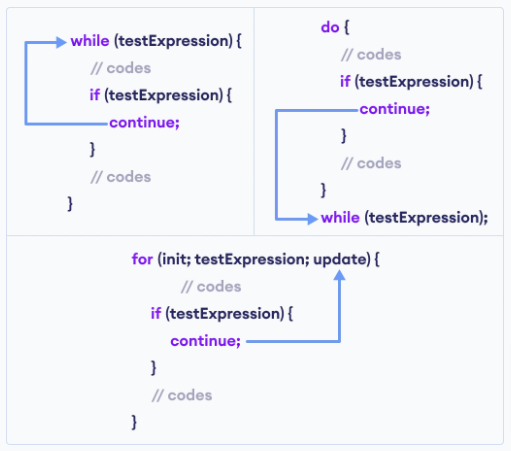
Continue Statement Example
class ContinueStatement{
public static void main(String args[]){
for(int i = 1; i<=10; i++){
if(i%2 == 0)
continue;
//print odd values.
System.out.print(i+ " ");
}
}
}
Output:
1 3 5 7 9
Java Continue Statement with Nested Loop
In terms of java nested loops, the continue statement jumps the current iteration of the innermost loop.
Working of Java Continue Statement with Nested Loops:

Example of Continue with Nested Loop:
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1, j = 1;
// outer loop
while (i <= 3) {
System.out.println("Outer Loop: " + i);
// inner loop
while(j <= 3) {
if(j == 2) {
j++;
continue;
}
System.out.println("Inner Loop: " + j);
j++;
}
i++;
}
}
}
Output:
Outer Loop: 1 Inner Loop: 1 Inner Loop: 3 Outer Loop: 2 Outer Loop: 3
Java Continue Statement with Labeled for Loop
As with the break statement, the continue may also specify a label to describe which enclosing loop to continue. Here is an example that demonstrates the use of a continue statement with a label inside an inner for loop.
Example of Labeled Continue Statement:
class LabelContinue{
public static void main(String args[]){
aa:
for(int i = 1; i<=3; i++){
bb:
for(int j = 1; j<=3; j++){
if(i==2 && j==2){
continue aa;
}
System.out.println(i+ " " +j);
}
}
}
}
Output:
1 1 1 2 1 3 2 1 3 1 3 2 3 3
Java Continue Statement with Inner Loop
In case, we use the continue statement inside the inner loop, then it continues the inner loop only. Let’s see the example program and understand the concept carefully:
Example on Continue with Inner Loop:
//Java Program to illustrate the use of continue statement
//inside an inner loop
public class ContinueExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//outer loop
for(int i=1;i<=3;i++){
//inner loop
for(int j=1;j<=3;j++){
if(i==2&&j==2){
//using continue statement inside inner loop
continue;
}
System.out.println(i+" "+j);
}
}
}
}
Output:
1 1 1 2 1 3 2 1 2 3 3 1 3 2 3 3
Java Continue Statement in while loop
We use the while loop when the number of iteration is not fixed. So, check out the example on java continue with while loop and grasp thoroughly.
Example on Java Continue statement inside While loop:
// Java Program to illustrate the use of continue statement
// inside the While loop
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initializing a variable say it count to a value
// greater than the value greater among the loop
// values
int count = 20;
// While loop for iteration
while (count >= 0) {
if (count == 7 || count == 15) {
count--;
// Decrementing variable initialized above
// Showing continue execution inside loop
// skipping when count==7 or count==15
continue;
}
// Printing values after continue statement
System.out.print(count + " ");
// Decrementing the count variable
count--;
}
}
}
Output:
20 19 18 17 16 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Java Continue Statement in do-while loop
A do-while loop is as same as the while loop, but it holds one dissimilarity. In a while loop, the condition is estimated before the execution of the loop’s body however in a do-while loop, the condition is assessed after the execution of the loop’s body. Check the sample program from the below section:
Continue Statement in Java Example in Do-While loop
public class ContinueExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
int i=1;
do
{
if (i==5)
{
i++;
continue;
}
System.out.print(i+ " ");
i++;
}while(i<10);
}
}
Output:
1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9

