Hashset initialization java: The HashSet class in Java is the first implementation class of the Set interface. It is used to creates a collection that uses a hash table for storage. A hash table stores the information by using a mechanism called hashing. In the hashing technique, the informational content of the key is used to determine a unique value, called its hash code. The hash code is used as the index at which the data associated with the key is stored.
This Tutorial on Java HashSet Class Contains:
- Creating a HashSet
- HashSet Hierarchy in Java
- Java HashSet vs HashMap
- Important Points about Java HashSet Class
- Difference between List and Set
- Constructors of Java HashSet Class
- Methods of HashSet Class in Java
- Insert Elements to HashSet Example
- Access HashSet Elements
- Remove Elements Java HashSet Example
- Finding Elements in Hash Set Java HashSet Example
- Java HashSet Example on Converting a Hash Set into a List/ArrayList
Creating a HashSet
For creating a HashSet Class in Java, firstly, we need to import the java.util.HashSet package.
After importing the package, take a look at the below & understand how we can create hash sets in Java.
// HashSet with 9 capacity and 0.75 load factor
HashSet<Integer> numerals= new HashSet<>(9, 0.75);Here, we have built a hash set named numerals
See, the part new HashSet<>(9, 0.75). The first parameter is capacity, and the second parameter is load factor.
- capacity: The capacity of this hash set is 9. Thus, it can store 9 elements.
- loadFactor: The load factor of this hash set is 0.6. This means, whenever our hash set is filled by 60%, the elements are moved to a new hash table of double the size of the original hash table.
Default Capacity and Load factor
Probably to create a hash table without defining its capacity and load factor is possible. For example,
// HashSet with default capacity and load factor HashSet<Integer> numbers1 = new HashSet<>();
By default,
- the capacity of the hash set will be 16
- the load factor will be 0.75
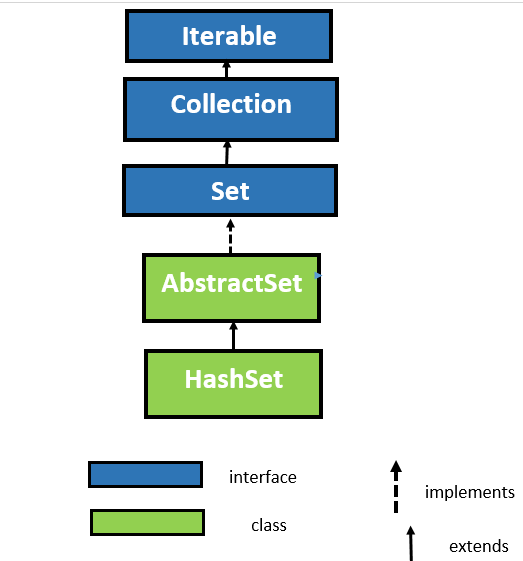
HashSet Hierarchy in Java
As you can observe in the below image of HashSet Java Hierarchy. The HashSet class performs the Set interface. Further, the Set interface inherits the Collection interface which ultimately extends the Iterable interface in a hierarchical order.
Java HashSet vs HashMap
| HashSet | HashMap |
| Implements java.util.Set interface | Implements java.util.Map |
| Allows a single null value | Allows a single null key and any number of null values |
| HashSet use add() method for add or storing data | HashMap use put() method for storing data |
| Doesn’t allow duplicate elements | Doesn’t allow duplicate keys but you can store duplicate values |
| Stores data as objects | Stores data in the form of key-value pair |
| HashSet needs just one parameter for its object initialization | It needs two parameters (key, value) for its object initialization |
Important Points about Java HashSet Class
- The underlying data structure for the hash set is the hash table.
- In HashSet, duplicates are not allowed.
- Insertion order is not preserved, elements are stored on the basis of their hash code.
- HashSet allows you to add heterogeneous elements.
- In HashSet, null insertion is possible.
- It implements a Serializable and Clonable interface but doesn’t implement a RandomAccess interface.
- HashSet is the best for search operations.
Difference between List and Set
A Set holds unique elements only whereas a List can hold duplicate elements.
Constructors of Java HashSet Class
There are 4 constructors are available in the Java HashSet class, which are described below:
1. HashSet(): This constructor creates a default hash set.
2. HashSet(int capacity): It is used to initialize the capacity of the hash set to the given capacity.
3. HashSet(int capacity, float load factor): This constructor is used to initialize the capacity of the hash table to the given capacity and the given load factor.
4. HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c): It is used to initializes the hash set by using the elements of collection c.
Methods of HashSet Class in Java
The HashSet Class offers different methods that permit us to perform several operations on the set.
1. boolean add(Element e): This method is used to add the element in the hash set.
2. void clear(): This method is used to remove all the elements from the hash set.
3. boolean contains(Element e): This method is used to check whether the specified element present in the hash set or not. If the element found in the hash set then it returns true otherwise it returns false.
4. boolean isEmpty(): This method is used to check the hash set is empty or not. If it is empty it returns true else returns false.
5. int size(): This method returns the number of elements from the hash set.
6. boolean remove(Element e): This method is used to remove the specified element from the hash set.
7. Object clone(): This method is used to returns a shallow copy of the hash set.
Insert Elements to HashSet Example
import java.util.*;
class hashSetExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
//creating a hash set
HashSet hset = new HashSet();
//adding elements in hash set
hset.add("Amit");
hset.add("Sumit");
hset.add("Rohit");
hset.add("Virat");
hset.add("Vijay");
//adding duplicate elements in hash set
hset.add("Amit");
hset.add("Virat");
//adding null value in hash set
hset.add(null);
hset.add(null);
//displaying hash set elements
System.out.println("Elements in the hash set are: " +hset);
}
}
Output:
Elements in the hash set are: [null, Rohit, Vijay, Amit, Sumit, Virat]
Access HashSet Elements
To access the elements of a hash set, we will make use of the iterator() method. To utilize this HashSet method, we must import the java.util.Iterator package. For illustration,
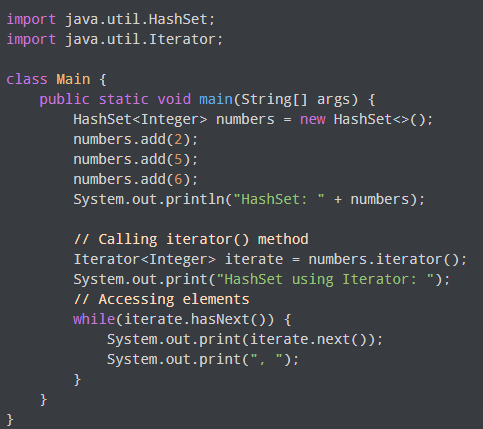
Output:
HashSet: [2, 5, 6] HashSet using Iterator: 2, 5, 6,
Remove Elements Java HashSet Example
import java.util.*;
class hashSetExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
//creating a hash set
HashSet hset = new HashSet();
//adding elements in hash set
hset.add("Amit");
hset.add("Sumit");
hset.add("Rohit");
hset.add("Virat");
hset.add("Vijay");
hset.add(null);
System.out.println("Hash Set elements are: " +hset);
//removing a specific element from hash set
hset.remove("Amit");
System.out.println("After removing(Amit) HashSet element is: " +hset);
//removing all elements from hash set
hset.clear();
//displaying hash set elements
System.out.println("Elements in the hash set are: " +hset);
}
}
Output:
Hash Set elements are: [null, Rohit, Vijay, Amit, Sumit, Virat] After removing(Amit) Hash Set element is: [null, Rohit, Vijay, Sumit, Virat] Elements in the hash set are: []
Finding Elements in Hash Set Java HashSet Example
import java.util.*;
class hashSetExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
//creating a hash set
HashSet hset = new HashSet();
//adding elements in hash set
hset.add("Amit");
hset.add("Sumit");
hset.add("Rohit");
hset.add("Virat");
hset.add("Vijay");
//find the number of elements in the hash set
int elements = hset.size();
System.out.println("The size of the hash set is: " +elements);
}
}
Output:
The size of the hash set is: 5
Java HashSet Example on Converting a Hash Set into a List/ArrayList
import java.util.*;
class hashSetExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
//creating a hash set
HashSet hset = new HashSet();
//adding elements in hash set
hset.add("Amit");
hset.add("Sumit");
hset.add("Rohit");
hset.add("Virat");
hset.add("Vijay");
System.out.println("Hash Set element is: " +hset);
//converting a hash set into an array list.
List alist = new ArrayList(hset);
System.out.println("ArrayList is: " +alist);
}
}
Output:
Hash Set elements are: [Rohit, Vijay, Amit, Sumit, Virat] ArrayList is: [Rohit, Vijay, Amit, Sumit, Virat]

