Logical operators in c: Logical Operators in C programming language combines multiple boolean expressions. If we want to check more than one condition, then we need logical Operators.
Logical Operators always produces boolean results, either TRUE(non-zero value) or FALSE(zero value).
There are 3 logical operators in C language AND(&&), OR(||) and NOT(!)
For Example
“If Humidity is less than 10% and Temperature is more than 30 degree celsius”
We can implement above mentioned condition using logical operator as follows:
if((Humidity < 10) && (Temperature > 30))
Description of Logical Operators in C
- AND : Returns true, If both operands are true otherwise false.
- OR : Returns false If both operands are false, otherwise true.
- NOT : Returns true if operand is false and Returns false if operand is true.
Here is the truth table of Logical Operators
| A | B | A && B | A || B | !A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRUE | FALSE | FALSE | TRUE | FALSE |
| TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE |
| FALSE | TRUE | FALSE | TRUE | TRUE |
| FALSE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE | TRUE |
C Program to show use of Logical Operators
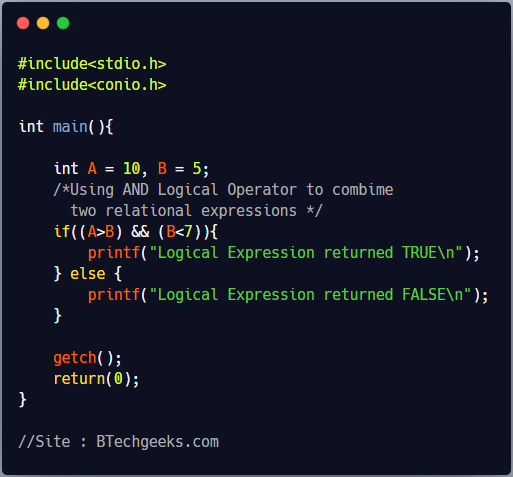
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main(){
int A = 10, B = 5;
/*Using AND Logical Operator to combime
two relational expressions */
if((A>B) && (B<7)){
printf("Logical Expression returned TRUE\n");
} else {
printf("Logical Expression returned FALSE\n");
}
getch();
return(0);
}
Output
Logical Expression returned TRUE
