Data abstraction is defined as the process of hiding the internal details from the user and showing only functionality. Consider a real-world example of a man driving a car. When a man driving a car he pressing the accelerators to increase the car speed and applying the brake to stop the car but he doesn’t know how pressing the accelerators will increase the car speed and applying the brake will stop the car. The man doesn’t know the inner mechanism of a car. This is called abstraction. Data abstraction can be achieved through Abstract Class.
Before discussing Abstract Class in Java. We can recall you in C++ if a class has at least one pure virtual function then the class becomes an abstract class. We can make an abstract class in C++ with the help of the virtual keyword. But in java, there is no virtual Keyword.
- How to Create Abstract Class in Java?
- Important Points about Java Abstract class
- Rules to Declare Abstract Class in Java
- Features of Abstract Class in Java
- How to Achieve Abstraction in Java?
- Difference between Interface and Abstract Class in Java
- Advantages of Abstract Class in Java
- Disadvantages of Abstract Class in Java
- Abstract Method and Class in Java
- Why we Use Abstract Class in Java?
- Abstract Class in Java Example
- Abstract Class with Constructor Example Program
- Abstract Class without Abstract Method Example
How to Create Abstract Class in Java?
In Java, we can create an abstract class with the help of the abstract keyword. Like C++, in Java, an abstract class cannot be instantiated (instance cannot be created). But we can create a reference variable of an abstract class.
Syntax:
abstract class class_name { }
Important Points about Java Abstract class
- We can create an abstract class with the help of the abstract keyword.
- We cannot instantiate an abstract class. But we can create a reference for an abstract class.
- Abstract class contains abstract and non-abstract methods.
- If a class has an abstract method then it must be declared that class as abstract.
- An abstract class contains a constructor.
- An abstract class also has final methods. (methods can’t be overridden).
- An abstract class is a way to achieve abstraction (not 100 percent).
- Abstraction is an OOPs concept that is used to hide the implementation details from the user.
Do Read:
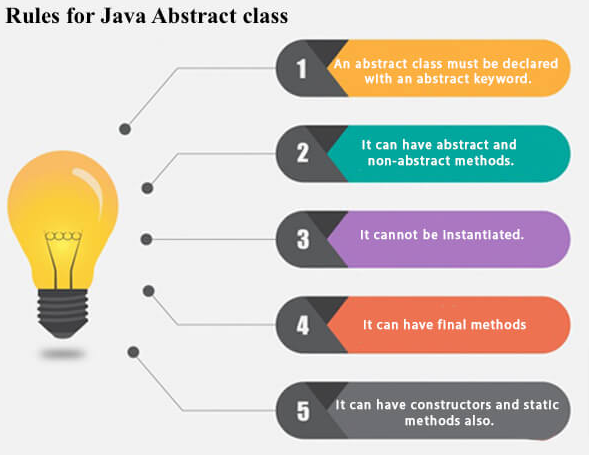
Rules to Declare Abstract Class in Java
There are certain pointers to be kept in mind while dealing with Abstract Class in Java and they are as mentioned below.
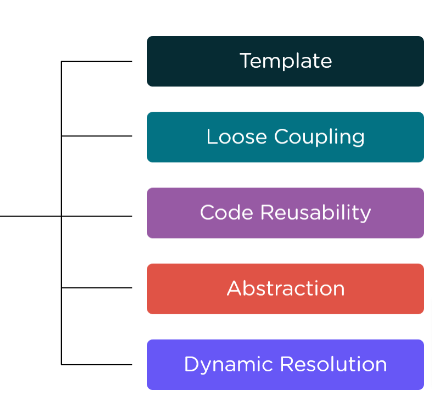
Features of Abstract Class in Java
There are few characteristics of a Java Abstract Class and they are mentioned in detail below.
Template: Abstract Class in Java provides the best way to execute the data abstraction process and gives developers an option to hide the code implementation. In addition, it provides the end-user a template and explains the methods included.
Loose Coupling: Data Abstraction in Java enables loose coupling and reduces dependencies at an exponential level.
Code Reusability: Utilizing Abstract Class in the Code can save a lot of time as we can call the abstract method as and when the method is needed. It avoids the process of writing the same code again and again.
Abstraction: Java Data Abstraction helps the developers to hide the code complications from the end-users and reduces the project’s complete characteristics to necessary components.
Dynamic Resolution: Taking help from the dynamic method resolution developers can solve various complexities using one abstract method.
How to Achieve Abstraction in Java?
You can achieve abstraction in Java using two different methods one is through Abstract Class and the other is through Interface.
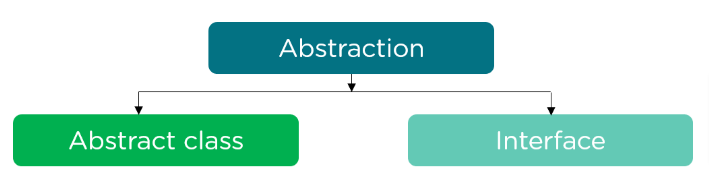
Interface: Interface in Java is defined as a boundary between the method and the class implementing it. Interface in Java holds a method signature in it but not the implementation of the method. We use Interface to Achieve Abstraction in Java.
//Syntax:
interface <Class_Name>{
//Method_Signatures;
}
Difference between Interface and Abstract Class in Java
Although Interface and Abstract Class in Java Perform Similar Operations there are certain minute differences between the two and they are outlined as follows
| Interface | Abstract Class |
| Keyword used is interface | Keyword used is abstract |
| Multiple interfaces can be implemented | One abstract class can be extended |
| It Supports Multiple Inheritance | It Cannot support Multiple Inheritance |
| Subclasses can implement an interface | Subclasses need to extend abstract class |
Now, that we are familiar with the basic differences between Interface and Abstract Class in Java let’s dive into the further sections and learn some of the advantages and disadvantages of Java Abstract Class.
Advantages of Abstract Class in Java
Go through the below-provided advantages of Java Abstract Class and they are as under
- Abstract Class is necessary for writing shorter codes.
- It helps you to avoid duplicate codes.
- Abstract Classes enables code reusability.
- You can make changes to Internal Code Implementation without affecting the Classes.
In addition to the numerous advantages that come with Java Abstract Class, there are quite a few disadvantages too that you need to pay attention to. Let’s get into them and learn the cons too.
Disadvantages of Abstract Class in Java
- Abstraction in Java is Expensive as you need to handle cases and situations that aren’t always needed.
- Object-relational impedance Mismatch in case of RDBMS.
- In the case of frameworks like hibernate you will get Object Relational Mapping.
Abstract Method and Class in Java
- An abstract class can include methods that contain no implementations (methods without body) is known as abstract
- methods in java.
- Like an abstract class, abstract methods must be declared with abstract keywords.
- The abstract methods declaration must end with a semicolon rather than a block.
- Abstract methods must be created and declared in an abstract class.
- Abstract methods don’t have method implementation (method body) it has only method signature.
Example of abstract method: abstract void showMsg(); // Nobody
Why we Use Abstract Class in Java?
Let’s say we have a class Bank that has a method getRateOfInterest() and subclasses of it like OBC, SBI, and PNB. Since the Bank interest different from one bank to another bank, there is no point to implement this method in the Parent class (Bank class). This is because every child class ( like OBC class, SBI class, etc.) must override this method to give its own implementation details, like SBI class will say “SBI has 7 percent interest” and OBC class will say “OBC has 8 percent interest”.
So when we know that all the Bank child classes (SBI, OBC, and PNB, etc.) will and should override this method, then there is no point to implement this method in the parent class (Bank class). Thus, making this method abstract would be a good practice.
Now each Bank must have a rate of interest, by making this method abstract we made it compulsory to the child class (SBI, OBC, etc.) to give implementation details to this method. That’s why we use the Abstract Class.
Let’s understand this by a real-world scenario Bank Example:
Abstract Class in Java Example
abstract class Bank{
abstract int getRateOfInterest();
}
class OBC extends Bank{
int getRateOfInterest(){
return 7;
}
}
class PNB extends Bank{
int getRateOfInterest(){
return 8;
}
}
class SBI extends Bank{
int getRateOfInterest(){
return 9;
}
}
class Example{
public static void main(String args[]){
Bank obj;
obj = new OBC();
System.out.println("OBC Rate of interest is: " +obj.getRateOfInterest()+ "%");
obj = new PNB();
System.out.println("PNB Rate of interest is: " +obj.getRateOfInterest()+ "%");
obj = new SBI();
System.out.println("SBI Rate of interest is: " +obj.getRateOfInterest()+ "%");
}
}
Output:

Abstract Class with Constructor Example Program
Like any other class, an abstract class has a constructor, data members, and methods.
abstract class Car{
Car(){
System.out.println("Car is created");
}
abstract void running();
void changeColour(){
System.out.println("Car colour is changed");
}
}
class Maruti extends Car{
void running(){
System.out.println("Car is running safely");
}
}
class Practical{
public static void main(String args []){
Maruti obj = new Maruti();
obj.running();
obj.changeColour();
}
}
Output:

Abstract Class without Abstract Method Example
Abstract class contains a non-abstract method (normal method) with method definition.
abstract class Car{
public void running(){
System.out.println("Car is running");
}
}
class Practical extends Car{
public void marutiRunning(){
System.out.println("Maruti car is running");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Practical obj = new Practical();
obj.running();
obj.marutiRunning();
}
}
Output:


